Melatonin attenuates growth factor receptor signaling required for SARS-CoV-2 replication
Melatonin may attenuate SARS-CoV-2 replication
Abstract
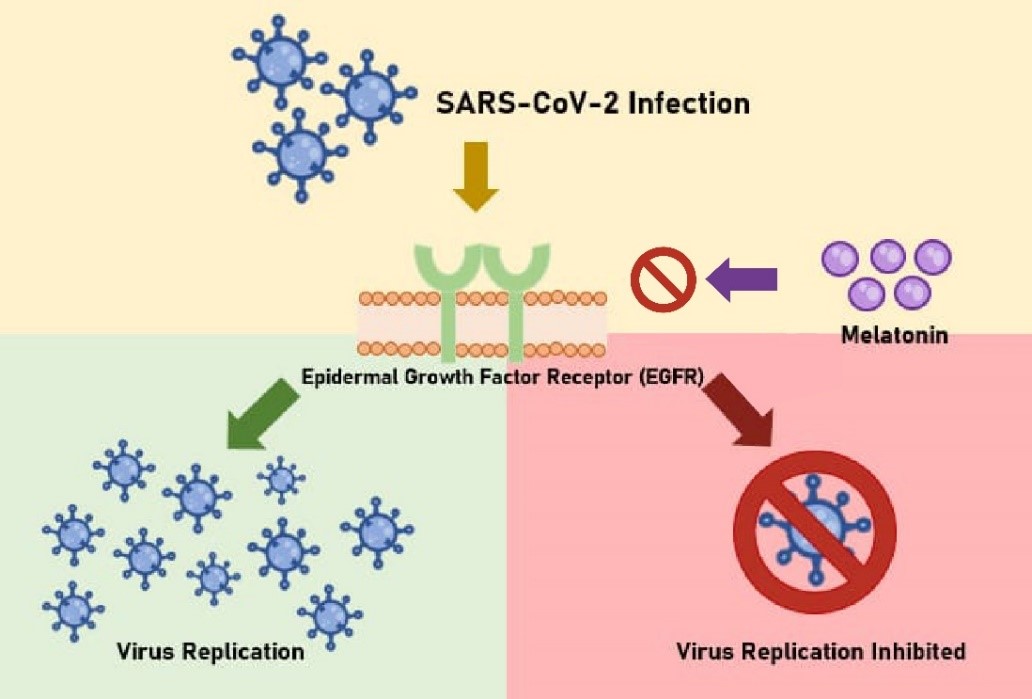
Melatonin has recently been suggested as a non-specific agent to prevent early (asymptomatic or moderate) infections with SARS-CoV-2 virus, the agent responsible for COVID-19, from developing to severe conditions requiring hospitalization. This recommendation was based on the ability of melatonin to suppress excessive inflammatory reactions and to modulate the immune system by attenuating the innate (blind and potentially harmful) response and potentiating the adaptive (selective and helpful) one. Recent data on the molecular mechanism of COVID-19 infection show that growth factor signaling is required for SARS-CoV-2 replication in the infected cells. When confronted with previously published data on the effects of melatonin on epidermal growth factor signaling, these data strongly suggest that melatonin can also act against the virus itself. Taken together, these data represent an additional argument in favor of using melatonin treatment as both a preventive and curative measure against COVID-19.
References
2. Niu Z, Li R (2020) Clinical study of novel coronavirus pneumonia prevention by melatonin. Reprod. Biomed. Online S1472-6483 (20): 30475-2. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2020.09.003.
3. Cos S, Blask DE (1994) Melatonin modulates growth factor activity in MCF‐7 human breast cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 17: 25-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079x.1994.tb00110.x.
4. Siu SW, Lau, KW, Tam PC, Shiu SY (2002) Melatonin and prostate cancer cell proliferation: interplay with castration, epidermal growth factor, and androgen sensitivity. Prostate 52: 106-122. doi: 10.1002/pros.10098.
5. Yun M, Kim EO., Lee D., Kim J-H, Kim J, Lee H, Kim S-H (2014) Melatonin sensitizes H1975 non-small-cell lung cancer cells harboring a T790M-targeted epidermal growth factor receptor mutation to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 34: 865-872. doi: 10.1159/000366305.
6. Yang S-F, Chen Y-S, Chien H-W, Wang K, Lin C-L, Chiou H-L, Lee C-Y, Chen P-N, Hsieh Y-H (2020) Melatonin attenuates epidermal growth factor-induced cathepsin S expression in ARPE-19 cells: Implications for proliferative vitreoretinopathy. J. Pineal Res. 68: e12615. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12615
7. Tan D-X, Hardeland R (2020) Potential utility of melatonin in deadly infectious diseases related to the overreaction of innate immune response and destructive inflammation: focus on COVID-19. Melatonin Res. 3: 120-143. doi: https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250052.
8. Zhang R, Wang X, Ni L, Di X, Ma B, Niu S, Liu C, and Reiter RJ (2020) COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment. Life Sci. 250: 117583. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117583.
9. Reiter RJ, Abreu-Gonzalez P, Marik PE, Dominguez-Rodriguez A (2020) Therapeutic algorithm for use of melatonin in patients with COVID-19. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 7: 226. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00226.
10. Tesarik J (2020) Melatonin to reduce death toll due to COVID-19: From innate to adaptive immune response. Glob. J. Med. Res.: K Interdisciplinary 20 (8): Version 1.0. doi: 10.34257/gjmrkvol20is8pg5.
11. Sekine T, et al. (2020) Robust T cell immunity in convalescent individuals with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19. Cell 183 (1): 158-168.e14. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.017.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


