Melatonin: A review of its physiopathological and therapeutic relationship with parasitic diseases
Melatonin and parasites
Abstract
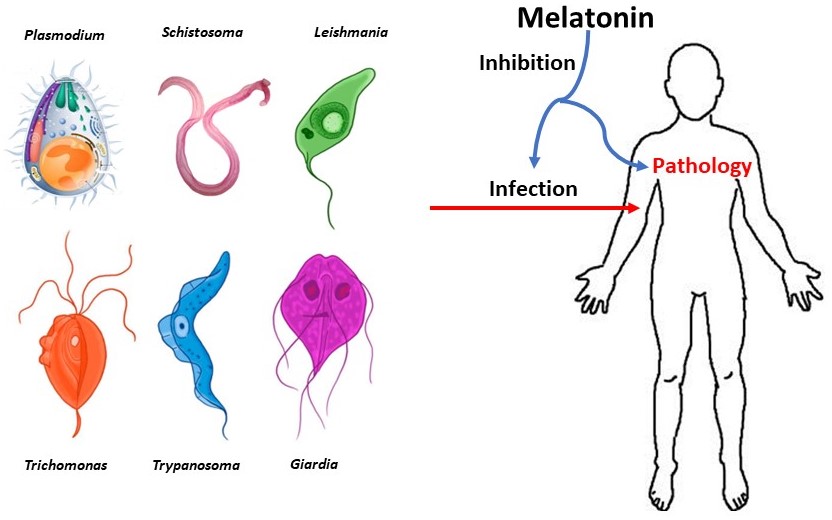
Melatonin (MEL), an indoleamine hormone synthesized in almost all organisms including humans, has been the object of a considerable body of research due to its pleiotropic functions. Recently, focus has been given to its roles as a regulator of the immune and inflammatory response, in the context of numerous disorders; likewise, it has been studied as a potential therapeutic option in numerous infectious diseases. In this sense, the relationship between this molecule and parasitic infections is of particular interest; thus, the present review aims to compile knowledge acquired in the last few years, regarding the participation of MEL in the pathophysiology of parasitic infections, and its potential clinical applications. Since parasitic diseases still represent a significant burden on health systems worldwide, particularly in low and lower-middle income countries with limited access to sanitation facilities and resources for therapeutic approaches, the continuing study of MEL, as an affordable and fundamentally safe healing option, might help better control of these infections.
References
2. Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Rosales-Corral S, Manchester LC (2013) The universal nature, unequal distribution and antioxidant functions of melatonin and its derivatives. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 13 (3): 373-384. doi: 10.2174/1389557511313030006.
3. Acuña-Castroviejo D, Escames G, Venegas C, Díaz-Casado ME, Lima-Cabello E, López LC, Rosales-Corral S, Tan D-X, Reiter R (2014) Extrapineal melatonin: sources, regulation, and potential functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71 (16): 2997-3025. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1579-2.
4. Tordjman S, Chokron S, Delorme R, Charrier A, Bellissant E, Jaafari N, Fougerou C (2017) Melatonin: pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 15 (3): 434-443. doi: 10.2174%2F1570159X14666161228122115.
5. Xie Z, Fei Chen F, Li WA, Geng X, Li C, Meng X, Feng Y, Liu W, Yu F (2017) A review of sleep disorders and melatonin. Neurol. Res. 39 (6): 559-565. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2017.1315864.
6. Vasey C, McBride J, Penta K (2021) Circadian rhythm dysregulation and restoration: the role of melatonin. Nutrients 13 (10): 3480. doi: 10.3390/nu13103480.
7. Zisapel N (2018) New perspectives on the role of melatonin in human sleep, circadian rhythms and their regulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 175 (16): 3190-3199. doi: 10.1111/bph.14116.
8. Lv WJ , Liu C, Yu LZ, Zhou JH, Li Y, Xiong Y, Guo A, Chao LM, Qu Q, Wei GW, Tang XG, Yin YL, Guo SN (2020) Melatonin alleviates neuroinflammation and metabolic disorder in DSS-induced depression rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020: 1241894. doi: 10.1155/2020/1241894.
9. Carrascal L, Nunez-Abades P, Ayala A, Cano M (2018) Role of melatonin in the inflammatory process and its therapeutic potential. Curr. Pharm. Des. 24 (14): 1563-1588. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180426112832.
10. Zefferino R, Di Gioia S, Conese M (2021) Molecular links between endocrine, nervous and immune system during chronic stress. Brain Behav. 11 (2): e01960. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1960.
11. Bonilla E, Valero N, Ponds H, Chacín-Bonilla L (1997) Melatonin protects mice infected with Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 53: 430–434. doi: 10.1007/s000180050051.
12. Bonilla E, Valero N, Chacín-Bonilla L, Medina-Leendertz S (2004) Melatonin and viral infections. J. Pineal Res. 36: 73–79. doi: 10.1046%2Fj.1600-079X.2003.00105.x.
13. Juybari KB, Pourhanifeh MH, Hosseinzadeh A, Hemati K, Mehrzadi S (2020) Melatonin potentials against viral infections including COVID-19: Current evidence and new findings. Virus Res. 287: 198108. doi: 10.1016%2Fj.virusres.2020.198108.
14. Anderson G, Reiter RJ (2020) Melatonin: roles in influenza, Covid‐19, and other viral infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 30 (3): e2109. doi: 10.1002%2Frmv.2109.
15. Roth JA, Kim BG, Lin WL, Cho MI (1999) Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 22041–22047. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.31.22041.
16. Hanikoglu A, Kucuksayan E, Akduman RC, Ozben T (2018) A review on melatonin's effects in cancer: potential mechanisms. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 18 (7): 985-992. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666171121120223.
17. Wang Z, Zhou F, Dou Y, Tian X, Liu C, Li H, Shen H, Chen G (2018) Melatonin alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced secondary brain injury in rats via suppressing apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and mitochondria injury. Transl. Stroke Res. 9 (1): 74-91. doi: 10.1007/s12975-017-0559-x.
18. Bondy SC, Campbell A (2018) Mechanisms underlying tumor suppressive properties of melatonin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (8): 2205. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082205.
19. Moniruzzaman M, Ghosal I, Das D, Chakraborty SB (2018) Melatonin ameliorates H2O2-induced oxidative stress through modulation of Erk/Akt/NFkB pathway. Biol. Res. 51: 17. doi: 10.1186/s40659-018-0168-5.
20. Rehman SU, Ikram M, Ullah N, Alam SI, Park HY, Badshah H, Choe K, Ok Kim M (2019) Neurological enhancement effects of melatonin against brain injury-induced oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration via AMPK/CREB signaling. Cells 8 (7): 760. doi: 10.3390/cells8070760.
21. Madhu LN, Kodali M, Attaluri S, Shuai B, Melissari L, Rao X, Shetty AK (2021) Melatonin improves brain function in a model of chronic Gulf War Illness with modulation of oxidative stress, NLRP3 inflammasomes, and BDNF-ERK-CREB pathway in the hippocampus. Redox Biol. 43: 101973. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101973.
22. Chitimus DM, Popescu MR, Voiculescu SE, Panaitescu AM, Pavel B, Zagrean L, Zagrean AM (2020) Melatonin’s impact on antioxidative and anti-inflammatory reprogramming in homeostasis and disease. Biomolecules 10 (9): 1211. doi: 10.3390/biom10091211.
23. Toader AM, Hoteiuc O, Bidian C, Oltean DD, Tabaran F, Grad O, Clichici S, Mitrea DR (2021) Neuronal apoptosis can be prevented by the combined therapy with melatonin and hypothermia in a neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Med. Pharm. Rep. 94 (2): 197. doi: 10.15386/mpr-1903.
24. Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Rosales-Corral S, Galano A, Zhou XJ, Xu B (2018) Mitochondria: central organelles for melatonin′ s antioxidant and anti-aging actions. Molecules 23 (2): 509. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020509.
25. Palagini L, Manni R, Aguglia E, Amore M, Brugnoli R, Bioulac S, Bourgin P, Micoulaud Franchi JA, Girardi P, Grassi L, Lopez R (2021) International expert opinions and recommendations on the use of melatonin in the treatment of insomnia and circadian sleep disturbances in adult neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Psychiatry 12: 688890. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.688890.
26. Fatemeh G, Sajjad M, Niloufar R, Neda S, Leila S, Khadijeh M (2022) Effect of melatonin supplementation on sleep quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 269 (1): 205-216. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10381-w.
27. Liu ZJ, Ran YY, Qie SY, Gong WJ, Gao FH, Ding ZT, Xi JN (2019) Melatonin protects against ischemic stroke by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization toward anti‐inflammatory phenotype through STAT3 pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 25 (12): 1353-1362. doi: 10.1111/cns.13261.
28. Li J, Liu H, Wang X, Xia Y, Huang J, Wang T, Lin Z, Xiong N (2022) Melatonin ameliorates Parkinson’s disease via regulating microglia polarization in a RORα‐dependent pathway. NPJ. Parkinsons Dis. 8 (1): 1-12. doi: 10.1038/s41531-022-00352-5.
29. Vasileva Z (2021) Melatonin and epilepsy. Folia Med. (Plovdiv) 63 (6): 827-833. doi: 10.3897/folmed.63.e58637.
30. Ferlazzo N, Andolina G, Cannata A, Costanzo MG, Rizzo V, Currò M, Ientile R, Caccamo D (2020) Is melatonin the cornucopia of the 21st century?. Antioxidants 9 (11): 1088. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111088.
31. Arias J, Meleán E, Valero N, Ponds H, Chacín-Bonilla L, Larreal Y, Bonilla E (2003) Efecto de la melatonina en la proliferación linfocitaria y la producción de interleucina 2 (IL-2) e interleucina 1 beta (IL-1β) en esplenocitos de ratones. Invest. Clin. 44: 41–50.
32. Carrillo-Vico A, Lardone PJ, Alvarez-Sánchez N, Rodríguez-Rodríguez A, Guerrero JM (2013) Melatonin: buffering the immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14: 8638–8683. doi: 10.3390/ijms14048638.
33. Hardeland R (2018) Melatonin and inflammation-Story of a double-edged blade. J. Pineal Res. 65 (4): e12525. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12525.
34. Hardeland R (2019) Aging, melatonin, and the pro-and anti-inflammatory networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (5): 1223. doi:10.3390/ijms20051223.
35. Suofu Y, Li W, Jean-Alphonse FG, Jia J, Khattar NK, Li J, Baranov SV, Leronni D, Mihalik AC, He Y, Cecon E, Wehbi VL, Kim J, Heath BE, Baranova OV, Wang X, Gable MJ, Kretz ES, Di Benedetto G, Lezon TR, Ferrando LM, Larkin TM, Sullivan M, Yablonska S, Wang J, Minnigh MB, Guillaumet G, Suzenet F, Richardson RM, Poloyac SM, Stolz DB, Jockers R, Witt-Enderby PA, Carlisle DL, Vilardaga JP, Friedlander RM (2017) Dual role of mitochondria in producing melatonin and driving GPCR signaling to block cytochrome c release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114 (38): E7997-E8006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705768114.
36. Zhao D, Yu Y, Shen Y, Liu Q, Zhao Z, Sharma R, Reiter RJ (2019) Melatonin synthesis and function: evolutionary history in animals and plants. Front. Endocrinol. 10: 249. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00249.
37. Nikolaev G, Robeva R, Konakchieva R (2021) Membrane melatonin receptors activated cell signaling in physiology and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (1): 471. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010471.
38. Li DY, Smith DG, Hardeland R, Yang MY, Xu HL, Zhang L, Yin HD, Zhu Q (2013) Melatonin receptor genes in vertebrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14: 11208–11223. doi:10.3390/ijms140611208.
39. Pala D, Lodola A, Bedini A, Spadoni G, Rivara S (2013) Homology models of melatonin receptors: challenges and recent advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14: 8093–8121. doi:10.3390/ijms14048093.
40. Negrette B, Bonilla E, Valero N, Pons H, Tamayo JG, Chacín-Bonilla L, Medina-Leendertz S, Añez F (2001) Melatonin treatment enhances the efficiency of mice immunization with Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus TC-83. Neurochem. Res. 26 (7): 767-770. doi: 10.1023/a:1011645400123.
41. Bonilla E, Valero N, Chacín-Bonilla L, Pons H, Larreal Y, Medina-Leendertz S, Marina Espina L (2003) Melatonin increases interleukin-1β and decreases tumor necrosis factor alpha in the brain of mice infected with the Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Neurochem. Res. 28 (5): 681-686. doi: 10.1023/a:1022897314108.
42. Medina S, Valero-Fuenmayor N, Chacin-Bonilla L, Anez F, Giraldoth D, Arias J, Espina G, Achong AY, Bonilla E (1999) Exposure to 2500 lux increases serum melatonin in Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis. Neurochem. Res. 24 (6): 775-778. doi: 10.1023/a:1020735730869.
43. Medina-Leendertz S, Valero N, Chacín-Bonilla L, Añez F, Giraldoth D, Arias J, Espina G, Díaz S, Bonilla E (2001) High intensity light increases olfactory bulb melatonin in Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection. Neurochem. Res. 26 (3): 231-234. doi: 10.1023/a:1010964500370.
44. Bonilla E, Rodón C, Valero N, Pons H, Chacín-Bonilla L, Tamayo JG, Rodríguez Z, Medina-Leendertz S, Añez F (2001) Melatonin prolongs survival of immunodepressed mice infected with the Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 95 (2): 207-210. doi: 10.1016/s0035-9203(01)90170-1.
45. Valero N, Meleán E, Bonilla E, Arias J, Espina LM, Chacin-Bonilla L, Larreal Y, Maldonado M, Anez F (2005) In vitro, melatonin treatment decreases nitric oxide levels in murine splenocytes cultured with the Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Neurochem. Res. 30 (11): 1439-1442. doi: 10.1007/s11064-005-8634-1.
46. Valero N, Nery A, Bonilla E, Espina LM, Chacin-Bonilla L, Anez F, Maldonado M, Meleán E (2009) Antagonistic effect of luzindole in mice treated with melatonin during the infection with the venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Neurochem. Res. 34 (2): 268-273. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9766-x.
47. Reiter RJ, Sharma R, Simko F, Dominguez-Rodriguez A, Tesarik J, Neel RL, Slominski AT, Kleszczynski K, Martin-Gimenez VM, Manucha W, Cardinali DP (2022) Melatonin: highlighting its use as a potential treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79 (3): 143. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04102-3.
48. Wongchitrat P, Yasawong M, Jumpathong W, Chanmanee T, Samutpong A, Dangsakul W, Govitrapong P, Reiter RJ, Puthavathana P (2022) Melatonin inhibits Zika virus replication in Vero epithelial cells and SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells. Melatonin Res. 5 (2): 171-185. doi: 10.32794/mr112500127.
49. Boga JA, Coto‐Montes A, Rosales‐Corral SA, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2012) Beneficial actions of melatonin in the management of viral infections: a new use for this “molecular handyman”?. Rev. Med. Virol. 22 (5): 323-338. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1714.
50. Chacín-Bonilla L, Dikdan Y (1981) Prevalencia de Entamoeba histolytica y otros parásitos intestinales en una comunidad suburbana de Maracaibo. Investigación Clínica 22 (4): 185 – 203.
51. Chacin de Bonilla L, Mathews HM, Healy GR, Dikdan Y, Rodriguez de Zambrano N (1984) Serologic and parasitologic studies of amebiasis in two suburban communities of Maracaibo, Venezuela. Investigación Clínica 25 (2): 69-80.
52. Chacín-Bonilla L (2013) Las enfermedades parasitarias intestinales como un problema de salud global. Investigación Clínica 54 (1): 1-4.
53. Chacín-Bonilla L (2017) Perfil epidemiológico de las enfermedades infecciosas en Venezuela. Investigación Clínica 58 (2): 103-105.
54. Honorio RI, Dias BKM, Przyborski JM, Garcia CR (2022) Melatonin as a microenvironmental cue for parasite development inside the host. Melatonin res. 5 (1): 84-100. doi: 10.32794/mr112500122.
55. Chacín-Bonilla L, Vielma JR, Bonilla E (2014) Should Melatonin be Considered a Complementary or Alternative Therapy against Parasitic Infections?. Epidemiol. 4: e117. doi: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000e117.
56. Vielma JR, Bonilla E, Chacín-Bonilla L, Mora M, Medina-Leendertz S, Bravo Y (2014) Effects of melatonin on oxidative stress, and resistance to bacterial, parasitic, and viral infections: a review. Acta trop. 137: 31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2014.04.021.
57. World Health Organization (2021) World malaria report 2021: available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240040496 (accessed on August 12th, 2022).
58. Ferguson NM (2018) Challenges and opportunities in controlling mosquito-borne infections. Nature 559 (7715): 490-497. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0318-5.
59. Alves E, Bartlett PJ, Garcia CR, Thomas AP (2011) Melatonin and IP3-induced Ca2+ release from intracellular stores in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum within infected red blood cells. J. Biol. Chem. 286: 5905–5912. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.188474.
60. Gazarini ML, Beraldo FH, Almeida FM, Bootman M, Da Silva AM, Garcia CR (2011) Melatonin triggers PKA activation in the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium chabaudi. J. Pineal Res. 50: 64–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00810.x.
61. Lima WR, Holder AA, Garcia CR (2013a) Melatonin signaling and its modulation of PfNF-YB transcription factor expression in Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14: 13704–13718. doi: 10.3390/ijms140713704.
62. Hotta CT, Gazarini ML, Beraldo FH, Varotti FP, Lopes C, Markus RP, Pozzan T, Garcia CR (2000) Calcium-dependent modulation by melatonin of the circadian rhythm in malarial parasites. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2 (7): 466-468. doi: 10.1038/35017112.
63. Beraldo FH, Almeida FM, da Silva AM, García CRS (2005) Cyclic AMP and calcium interplay as second messengers in melatonin-dependent regulation of Plasmodium falciparum cell cycle. J. Cell Biol. 170: 551–557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200505117.
64. Hotta CT, Markus RP, García CRS (2003) Melatonin and N-acetyl-serotonin cross the red blood cell membrane and evoke calcium mobilization in malarial parasites. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 36: 1583–1587. doi: 10.1590/S0100-879X2003001100016.
65. Furuyama W, Enomoto M, Mossaad E, Kawai S, Mikoshiba K, Kawazu S (2014) An interplay between 2 signaling pathways: melatonin-cAMP and IP3-Ca2+ signaling pathways control intraerythrocytic development of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 446 (1): 125-131. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.070.
66. Pecenin MF, Borges-Pereira L, Levano-Garcia J, Budu A, Alves E, Mikoshiba K, Thomas A, Garcia CRS. (2018) Blocking IP3 signal transduction pathways inhibits melatonin-induced Ca2+ signals and impairs P. falciparum development and proliferation in erythrocytes. Cell Calcium 72: 81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2018.02.004.
67. Dias BKM, Nakabashi M, Alves MRR, Portella DP, Dos Santos BM, Costa da Silva Almeida F, Ribeiro RY, Schuck DC, Jordão AK, Garcia CRS (2020) The Plasmodium falciparum eIK1 kinase (PfeIK1) is central for melatonin synchronization in the human malaria parasite. Melatotosil blocks melatonin action on parasite cell cycle. J. Pineal Res. 69 (3): e12685. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12685.
68. Srinivasan V, Mohamed M, Zakaria R, Ahmad AH, (2012a) Malaria, anti malarial drugs and the role of melatonin. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 12: 371–379. doi: 10.2174/187152612804142198.
69. Srinivasan V, Ahmad AH, Mohamed M, Zakaria R (2012b) Melatonin effects on Plasmodium life cycle: new avenues for therapeutic approach. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 6: 139–147. doi: 10.2174/187221412800604635.
70. Schuck DC, Jordão AK, Nakabashi M, Cunha AC, Ferreira VF, Garcia CR (2014) Synthetic indole and melatonin derivatives exhibit antimalarial activity on the cell cycle of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 78: 375-382. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.03.055.
71. Luthra T, Nayak AK, Bose S, Chakrabarti S, Gupta A, Sen S (2019) Indole based antimalarial compounds targeting the melatonin pathway: their design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 168: 11-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.019.
72. Lunga MJ, Chisango RL, Weyers C, Isaacs M, Taylor D, Edkins AL, Khanye SD, Hoppe HC, Veale CGL (2018) Expanding the SAR of nontoxic antiplasmodial indolyl-3-ethanone ethers and thioethers. Chem. Med. Chem. 13 (13): 1353-1362. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201800235.
73. Dangi P, Jain R, Mamidala R, Sharma V, Agarwal S, Bathula C, Thirumalachary M, Sen S, Singh S (2019) Natural product inspired novel indole based chiral scaffold kills human malaria parasites via ionic imbalance mediated cell death. Sci. Rep. 9 (1): 1-7. doi: 10.1038%2Fs41598-019-54339-z.
74. Mallaupoma LR, Dias BK, Singh MK, Honorio RI, Nakabashi M, Kisukuri CD, Paixão MW, Garcia CR (2022) Decoding the Role of Melatonin Structure on Plasmodium falciparum Human Malaria Parasites Synchronization Using 2-Sulfenylindoles Derivatives. Biomolecules 12 (5): 638. doi: 10.3390/biom12050638.
75. Pasaje CF, Cheung V, Kennedy K, Lim EE, Baell JB, Grin MD, Ralph SA (2016) Selective inhibition of apicoplast tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase causes delayed death in Plasmodium falciparum. Sci. Rep. 6: 27531. doi: 10.1038/srep27531.
76. Scarpelli PH, Tessarin-Almeida G, Viçoso KL, Lima WR, Borges-Pereira L, Meissner KA, Wrenger C, Raffaello A, Rizzuto R, Pozzan T, Garcia CRS (2019) Melatonin activates FIS1, DYN1, and DYN2 Plasmodium falciparum related-genes for mitochondria fission: Mitoemerald-GFP as a tool to visualize mitochondria structure. J. Pineal Res. 66 (2): e12484. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12484.
77. Lima WR, Moraes M, Alves E, Azevedo MF, Passos DO, Garcia CR (2013b) The PfNF-YB transcription factor is a downstream target of melatonin and cAMP signaling in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J. Pineal Res. 54: 145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01021.x.
78. Lima WR, Tessarin-Almeida G, Rozanski A, Parreira KS, Moraes MS, Martins DC, Hashimoto RF, Galante PAF, Garcia CRS (2016) Signaling transcript profile of the asexual intraerythrocytic development cycle of Plasmodium falciparum induced by melatonin and cAMP. Genes Cancer 7 (9-10): 323-339. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.118.
79. Koyama FC, Ribeiro RY, Garcia JL, Azevedo MF, Chakrabarti D, Garcia CRS (2012) Ubiquitin proteasome system and the atypical kinase PfPK7 are involved in melatonin signaling in Plasmodium falciparum. J. Pineal Res. 53: 147–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.00981.x.
80. Koyama FC, Azevedo MF, Budu A, Chakrabarti D, Garcia CR (2014) Melatonin-induced temporal up-regulation of gene expression related to ubiquitin/proteasome system (UPS) in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15 (12): 22320-22330. doi: 10.3390/ijms151222320.
81. Singh MK, Tessarin-Almeida G, Dias BKM, Pereira PS, Costa F, Przyborski JM, Garcia CRS (2021) A nuclear protein, PfMORC confers melatonin dependent synchrony of the human malaria parasite P. falciparum in the asexual stage. Sci. Rep. 11 (1): 2057. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81235-2.
82. Guha M, Maity P, Choubey V, Mitra K, Reiter RJ, Bandyopadhyay U (2007) Melatonin inhibits free radical-mediated mitochondrial-dependent hepatocyte apoptosis and liver damage induced during malarial infection. J. Pineal Res. 43: 372–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00488.x.
83. Ataide BJdA, Kauffmann N, Mendes NdSF, Torres MLM, dos Anjos LM, Passos AdCF, de Moraes SAS, Batista EdJO, Herculano AM, Oliveira KRHM (2020) Melatonin prevents brain damage and neurocognitive impairment induced by Plasmodium berghei ANKA infection in murine model of cerebral malaria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 10: 541624. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.541624.
84. Srinivasan V, Spence DW, Moscovitch A, Pandi-Perumal SR, Trakht I, Brown GM, Cardinali DP (2010) Malaria: therapeutic implications of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 48: 1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00728.x.
85. Kedarisetty CK, Samaga BL, Vidyasagar S, Venkataraman J (2020) Oral melatonin improves the detection of parasitemia in malaria. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 14 (11): 1327-1331. doi: 10.3855/jidc.12518.
86. Macias M, Rodriguez-Cabezas MN, Reiter RJ, Osuna A, Acuña-Castroviejo D (1999) Presence and effects of melatonin in Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Pineal Res. 27: 86–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.1999.tb00601.x.
87. Santello FH, Frare EO, dos Santos CD, Toldo MP, Kawasse LM, Zucoloto S, doPrado Jr JC (2007) Melatonin treatment reduces the severity of experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J. Pineal Res. 42: 359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00427.x.
88. Santello FH, Frare EO, Caetano LC, Alonso Toldo MP, do Prado Jr JC, 2008. Melatonin enhances pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and protects against Chagas disease. J. Pineal Res. 45: 79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00558.x.
89. Kuehn CC, Rodrigues Oliveira LG, Santos CD, Ferreira DS, Alonso Toldo MP, de Albuquerque S, do Prado Jr JC (2009) Melatonin and dehydroepiandrosterone combination: does this treatment exert a synergistic effect during experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection?. J. Pineal Res. 47: 253–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00708.x.
90. Oliveira LG, Kuehn CC, Santos CD, Toldo MP, do Prado Jr JC (2010) Enhanced protection by melatonin and meloxicam combination in experimental infection with Trypanosoma cruzi. Parasite Immunol. 32: 245–251. doi: 10.1139/y02-052.
91. Brazão V, Colato RP, Santello FH, Vale GTD, Gonzaga NA, Tirapelli CR, Prado Jr JCD (2018) Effects of melatonin on thymic and oxidative stress dysfunctions during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J. Pineal Res. 65 (3): e12510. Doi: 10.1111/jpi.12510.
92. Brazao V, Del Vecchio Filipin M, Santello FH, Caetano LC, Abrahao AA, Toldo MP, do Prado Jr JC (2011) Melatonin and zinc treatment: distinctive modulation of cytokine production in chronic experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Cytokine 56: 627–632. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.08.037.
93. Brazão V, Filipin Mdel V, Santello FH, Azevedo AP, Toldo MP, de Morais FR, do Prado Jr JC (2015) Immunomodulatory properties and anti-apoptotic effects of zinc and melatonin in an experimental model of chronic Chagas disease. Immunobiology 220 (5): 626-633. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.11.018.
94. Cardinali DP, Alvarez CB (2011) Melatonin in Chagas’ disease. Possible therapeutic value. Medicina (B Aires) 71: 477–483.
95. Martin-Cano FE, Camello-Almaraz C, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Pozo MJ, Camello PJ (2013) Age-related changes in mitochondrial of mouse colonic smooth muscle: beneficial effects of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 56 (2): 163-174. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12109.
96. Oliveira LG, Kuehn CC, dos Santos CD, Miranda MA, da Costa CM, Mendonca VJ, do Prado Jr JC (2013) Protective actions of melatonin against heart damage during chronic Chagas disease. Acta. Trop. 128: 652–658. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.09.014.
97. Providello MV, Portapilla GB, Oliveira PAS, da Silva CBP, Anchieta NF, Tirapelli CR, de Albuquerque S (2021) Melatonin decreases circulating Trypanosoma cruzi load with no effect on tissue parasite replication. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 99 (8): 795-802. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2020-0473.
98. Milne G, Webster JP, Walker M (2020) Toxoplasma gondii: an underestimated threat? Trends Parasitol. 36 (12): 959-969. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2020.08.005.
99. Chacín-Bonilla L, Sánchez Y, Monsalve F, Estévez J (2001) Sero epidemiology of toxoplasmosis in Amerindians from Western Venezuela. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 65 (2): 131–135. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2001.65.131.
100. Chacín-Bonilla L, Sánchez Y, Estévez J, Larreal Y, Molero E (2003) Prevalence of human toxoplasmosis in San Carlos Island, Venezuela. Interciencia 28 (8): 457-462.
101. Baltaci AK, Bediz CS, Mogulkoc R, Kurtoglu E, Pekel A (2003) Effect of zinc and melatonin supplementation on cellular immunity in rats with toxoplasmosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 96: 237–245. doi: 10.1385/bter:96:1-3:237.
102. Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R, Turkoz Y, Bediz CS, Ozugurlu F (2004) The effect of pinealectomy and zinc deficiency on nitric oxide levels in rats with induced Toxoplasma gondii infection. Swiss Med. Wkly. 134: 359–363.
103. Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R, Bediz CS, Pekel A (2005) Effects of zinc deficiency and pinealectomy on cellular immunity in rats infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 104: 47–56. doi: 10.1385/bter:104:1:047.
104. Avunduk AM, Avunduk MC, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R (2007) Effect of melatonin and zinc on the immune response in experimental Toxoplasma retinochoroiditis. Ophtalmologica 221: 421–425. doi: 10.1159/000107504.
105. Machado NI, Dos Santos TAT, de Souza W, DaMatta RA, Seabra SH (2020) Treatment with melatonin induces a reduction of Toxoplasma gondii development in LLC-MK2 cells. Parasitol. Res. 119 (8): 2703-2711. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06766-5.
106. Dincel GC, Atmaca HT (2015) Nitric oxide production increases during Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 156: 104-112. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2015.06.009.
107. Al-Kuraishi AH, Khalil HI, Hasan HH, Al-Kuraishy HM (2021) Are alterations in melatonin and inflammatory cytokine serum levels linked with recurrent abortion in pregnant women with acute toxoplasmosis: The interacted nexus. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 71 (Suppl 8) (12): S22-S26.
108. Majumdar T, Sharma S, Kumar M, Hussain MA, Chauhan N, Kalia I, Sahu AK, Rana VS, Bharti R, Haldar AK, Singh AP, Mazumder S (2019) Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway attenuates β-catenin-dependent pro-parasitic role of STING-TICAM2-IRF3-IDO1 signalosome in Toxoplasma gondii infection. Cell Death Dis. 10 (3): 161. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1420-9.
109. WHO. Leishmaniasis Fact sheets. January 2022. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis. (Accessed on January 12th, 2023).
110. Laranjeira-Silva MF, Zampieri RA, Muxel SM, Floeter-Winter LM, Markus RP (2015) Melatonin attenuates Leishmania (L.) amazonensis infection by modulating arginine metabolism. J. Pineal Res. 59 (4): 478-487. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12279.
111. Parvez S, Yadagiri G, Arora K, Javaid A, Kushwaha AK, Singh OP, Sundar S, Mudavath SL (2021) Coalition of biological agent (melatonin) with chemotherapeutic agent (amphotericin B) for combating visceral leishmaniasis via oral administration of modified solid lipid nanoparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00859.
112. Fernandes JCR, Aoki JI, Maia Acuña S, Zampieri RA, Markus RP, Floeter-Winter LM, Muxel SM (2019) Melatonin and Leishmania amazonensis infection altered miR-294, miR-30e, and miR-302d impacting on Tnf, Mcp-1, and Nos2 expression. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 9: 60. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00060.
113. Zamani S, Hoseini AZ, Namin AM (2019) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity can modulate macrophage response to Leishmania major infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 69: 178-183. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.028.
114. Elmahallawy EK, Jiménez-Aranda A, Martínez AS, Rodriguez-Granger J, Navarro-Alarcón M, Gutiérrez-Fernández J, Agil A (2014) Activity of melatonin against Leishmania infantum promastigotes by mitochondrial dependent pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 220: 84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.06.016.
115. Minetti C, Chalmers RM, Beeching NJ, Probert C, Lamden K (2016) Giardiasis. BMJ. 27: 355. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i5369.
116. Pereira QLC, Hara CCP, Fernandes RTS, Fagundes DLG, França-Botelho ADC, Gomes MA, França EL, Honorio-França AC (2018) Human colostrum action against Giardia lamblia infection influenced by hormones and advanced maternal age. Parasitol. Res. 117 (6): 1783-1791. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-5860-4.
117. Al-Hadraawy SK, Al-ghurabi ME, Al-musawi MM, Alzeyadi M (2016) Ghrelin and melatonin as biomarkers in patients with giardiasis. Biotechnol.Biotechnol. Equip. 30 (3): 553-557. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2016.1149038.
118. Chacin-Bonilla L, Mathews H, Dikdan Y, Guanipa N (1990) Estudio seroepidemiológico de la amibiasis en una comunidad del estado Zulia, Venezuela. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 32 (6): 467-473.
119. Chacín-Bonilla L (2010) Amibiasis: Implicaciones del reconocimiento de Entamoeba dispar y de la identificación de Entamoeba moshkovskii en humanos. Invest. Clin. 51 (2): 239-256.
120. Carrero JC, Reyes-López M, Serrano-Luna J, Shibayama M, Unzueta J, Leon-Sicairos N, de la Garza M (2020) Intestinal amoebiasis: 160 years of its first detection and still remains as a health problem in developing countries. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 310 (1): 151358. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2019.151358.
121. Franca Botelho AC, Franca JL, Oliveira FMS, Franca EL, Honorio-Franca AC, Caliari MV, Gomes MA (2011) Melatonin reduces the severity of experimental amoebiasis. Parasit. Vectors 4: 62. doi: 10.1186%2F1756-3305-4-62.
122. Al-Hadraawy SK (2017) Study role of melatonin and leptin in patient infected with Entamoeba histolytica. Research Journal of Pharm. Technol. 10 (10): 3471-3473. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2017.00620.5.
123. Kristensson K, Claustrat B, Mhlanga JD, Møller M (1998) African trypanosomiasis in the rat alters melatonin secretion and melatonin receptor binding in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res. Bull. 47 (3): 265-269. doi: 10.1016/S0361-9230(98)00084-7.
124. El-Sokkary GH, Omar HM, Hassanein AF, Cuzzocrea S, Reiter RJ (2002) Melatonin reduces oxidative damage and increases survival of mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 32 (4): 319-332. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00753-5.
125. Laothong U, Pinlaor P, Hiraku Y, Boonsiri P, Prakobwong S, Khoontawad J, Pinlaor S (2010) Protective effect of melatonin against Opisthorchis viverrini‐induced oxidative and nitrosative DNA damage and liver injury in hamsters. J. Pineal Res. 49 (3): 271-282. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00792.x.
126. Laothong U, Pinlaor P, Boonsiri P, Pairojkul C, Priprem A, Johns NP, Charoensuk L, Intuyod K, Pinlaor S (2013) Melatonin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma and reduces liver injury in Opisthorchis viverrini‐infected and N‐nitrosodimethylamine‐treated hamsters. J. Pineal Res. 55 (3): 257-266. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12068.
127. Wongsena W, Charoensuk L, Dangtakot R, Pinlaor P, Intuyod K, Pinlaor S (2018) Melatonin suppresses eosinophils and Th17 cells in hamsters treated with a combination of human liver fluke infection and a chemical carcinogen. Pharmacol Rep. 70 (1): 98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.07.017.
128. Ximenes VF, Padovan CZ, Carvalho DA, Fernandes JR (2010) Oxidation of melatonin by taurine chloramine. J Pineal Res. 49 (2): 115-122. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00772.x.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


