The anxiolytic and analgesic effects of melatonin: a study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
The anxiolytic and analgesic effects of melatonin
Abstract
Anxiety and pain are both significant clinical challenges following surgery. Melatonin has been demonstrated to have both anxiolytic and analgesic effects in numerous experimental and clinical studies. This study protocol aims to present the design of a randomized study investigating the anxiolytic and analgesic effects of exogenous melatonin in cosmetic breast augmentation.
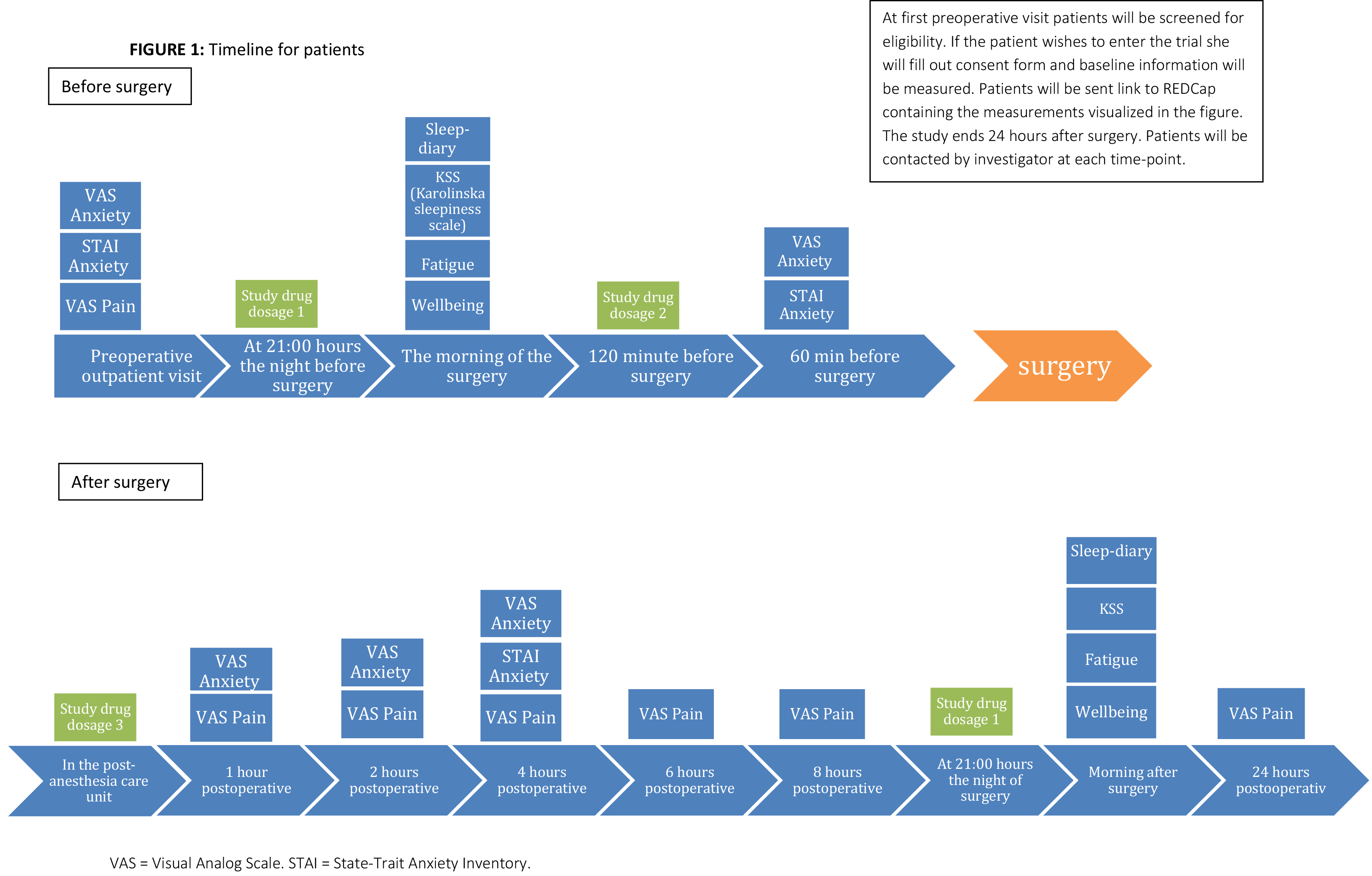
The study will be a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Included patients are candidates for primary breast augmentation or replacement of existing implants. Patients receive a standardized general anesthetic and postoperative analgesic regimen. The study medication includes 4 separate doses, containing either 10 mg of melatonin or placebo. Doses are administered orally at 21:00 hours of the night before surgery, 120 minutes before surgery, immediately after surgery in the post-anesthesia care unit, and at 21:00 hours of the night following surgery.
The two primary outcomes are preoperative anxiety, assessed by the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory and pain, measured by an integrated assessment of longitudinally measured pain intensity and opioid consumption. Secondary outcomes are VAS anxiety, and VAS pain, sleep quality, general fatigue and wellbeing.
This study protocol presents in detail the design of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study investigating the anxiolytic and analgesic effects of repeated doses of exogenous melatonin in patients undergoing cosmetic breast augmentation.
References
2. Stanley S-S, Hoppe I-C, Ciminello F-S (2012) Pain control following breast augmentation: a qualitative systematic review. Aesthet. Surg. J. 32: 964–972.
3. Rawal N, Gupta A, Helsing M, Grell K, Allvin R (2006) Pain relief following breast augmentation surgery: a comparison between incisional patient-controlled regional analgesia and traditional oral analgesia. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 23: 1010–1017.
4. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic Surgery Statistics Report 2017. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/
News/Statistics/2017/plastic-surgery-statistics-full-report-2017.pdf. (Accessed September 26, 2018).
5. Klein M, Gögenur I, Rosenberg J (2012) Postoperative use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with anastomotic leakage requiring reoperation after colorectal resection: cohort study based on prospective data. BMJ. 345: e6166.
6. Kehlet H (2005) Postoperative opioid sparing to hasten recovery: what are the issues? Anesthesiology. 102: 1083–1085.
7. Ashton H (1994) Guidelines for the rational use of benzodiazepines. When and what to use. Drugs. 48: 25‐40.
8. Brzezinski A (1997) Melatonin in humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 336: 186–195.
9. Srinivasan V, Pandi-Perumal S-R, Spence D-W, Moscovitch A, Trakht I et al. (2010) Potential use of melatonergic drugs in analgesia: mechanisms of action. Brain. Res. Bull. 81: 362–371.
10. Ochoa-Sanchez R, Rainer Q, Comai S, Spadoni G, Bedini A et al. (2012) Anxiolytic effects of the melatonin MT(2) receptor partial agonist UCM765: comparison with melatonin and diazepam. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 39: 318–325.
11. Andersen L-P, Werner M-U, Rosenberg J, Gögengur I (2014) A systematic review of peri-operative melatonin. Anaesthesia. 69: 1163–1171.
12. Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz K-F, Montori V Gøtzsche P-C et al. (2012) CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int. J. Surg. 10: 28–55.
13. Spielberger C-D, Gorsuch R-L, Lushene R, Vagg P-R, Jacobs G-A (1983) Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, California, USA.
14. Dai F, Silverman D-G, Chelly J-E, Li J, Belfer I, Qin L (2013) Integration of pain score and morphine consumption in analgesic clinical studies. J. Pain. 14: 767–777.
15. Akerstedt T, Gillberg M (1990) Subjective and objective sleepiness in the active individual. Int. J. Neurosci. 52: 29–37.
16. Christensen T, Bendix T, Kehlet H (1982) Fatigue and cardiorespiratory function following abdominal surgery. Br. J. Surg. 69: 417–419.
17. Caumo W, Schmidt A-P, Schneider C-N, Bergmann J, Iwamoto C-W et al (2001) Risk factors for postoperative anxiety in adults. Anaesthesia. 56: 720-728.
18. McCarthy C-M, Pusic A-L, Hidalgo D-A (2009) Efficacy of pocket irrigation with bupivacaine and ketorolac in breast augmentation: a randomized controlled trial. Ann. Plast. Surg. 62: 15–17.
19. Ong C-K, Lirk P, Tan J-M, Sow B-W (2005) The analgesic efficacy of intravenous versus oral tramadol for preventing postoperative pain after third molar surgery. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 63; 1162–1168.
20. Andersen LP, Gögenur I, Rosenberg J, Reiter R-J (2016) The Safety of Melatonin in Humans. Clin. Drug. Investig. 36: 169-175.
21. International Comitee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributers. http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authors-and-contributors.html (Accessed December 14, 2018).
22. Yousaf F, Seet E, Venkatraghavan L, Abrishami A, Chung F (2010) Efficacy and safety of melatonin as an anxiolytic and analgesic in the perioperative period: a qualitative systematic review of randomized trials. Anesthesiology. 113: 968–976.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


