The therapeutic potential of melatonin against hepatotoxicity caused by obesity and NSAIDs: A comprehensive review
Protective role of melatonin against hepatotoxicity
Abstract
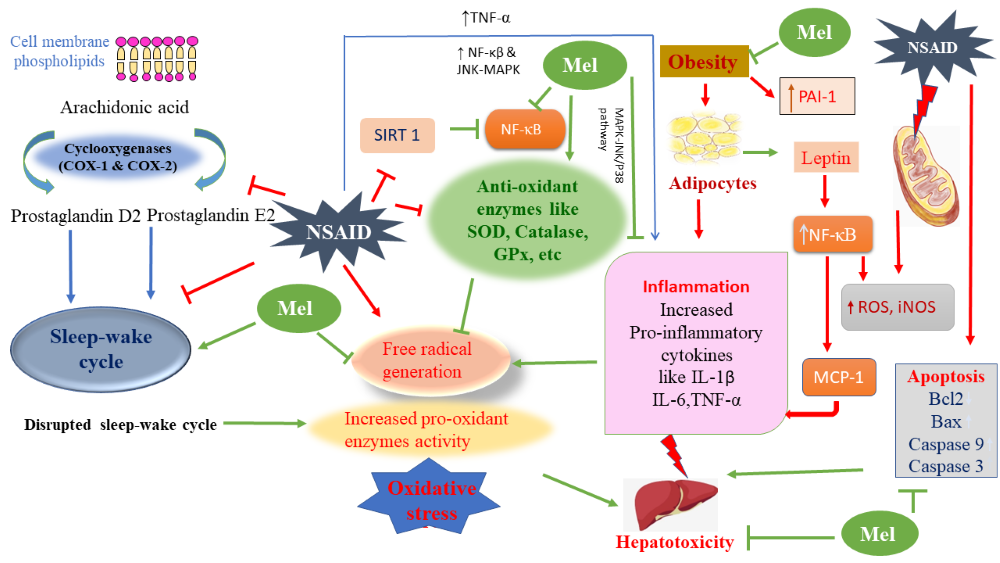
The obesity and increased free fatty acid level are considered the etiology of hepatotoxicity leading to steatohepatitis and hepatic fibrosis. Obesity promotes inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Adipocytes secrete various proinflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and leptin to initiate a vicious cycle and cause further fat accumulation and weight gain. Specifically, to liver, the fat accumulation will cause non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the most prevailing chronic liver ailment, if it is not properly treated, then it will cause severe outcomes including fatality. In addition, obesity also cause other inflammatory disorders including osteoarthritis of the knee, joint pain, etc. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are most often used medicines for treatment of inflammation but their serious side effects are concerning. These include gastric mucosal damage, liver injury with elevated aminotransferase (AST/ALT) levels, hepatitis, jaundice and more fatal liver diseases. Melatonin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory molecule can be used to treat diverse kind of inflammatory diseases. It remarkably reduces the mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, etc. Melatonin and its metabolites retain the properties as an effective free radical scavenger and regulate various antioxidative and pro-oxidative enzymes. This molecule can potentially abate the ill effects of hepatotoxicity induced by both NSAIDs and obesity. Therefore, this review briefly summarizes the recent available knowledge on the protective effects of melatonin against various disorders involving weight gain and hepatotoxicity.
References
2. Ma C, Avenell A, Bolland M, Hudson J, Stewart F, Robertson C, MacLennan G (2017) Effects of weight loss interventions for adults who are obese on mortality, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 359: j4849. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4849.
3. Anderson N, Borlak J (2008) Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets in steatosis and steatohepatitis. Pharmacol. Rev. 60 (3): 311-357. doi: 10.1124/pr.108.00001.
4. Kojima H, Sakurai S, Uemura M, Fukui H, Morimoto H, Tamagawa Y (2007) Mitochondrial abnormality and oxidative stress in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 31 (1Suppl): S61-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00288.x.
5. Fan JG, Kim SU, Wong VWS (2017) New Trends on Obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 67(4): 862-873. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.06.003.
6. Lementowski PW, Zelicof SB (2008) Obesity and osteoarthritis. Am. J. Orthop. 37 (3): 148-151. PMID: 18438470.
7. O'Connor N, Dargan PI, Jones AL (2003) Hepatocellular damage from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. QJM. 96 (11): 787–791. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcg138.
8. Lee CY (2013) The Effect of high-fat diet-induced pathophysiological changes in the gut on obesity: What should be the ideal treatment? Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 4 (7): e39 10.1038/ctg.2013.11.
9. Ohashi K, Shibata R, Murohara T, Ouchi N (2014) Role of anti-inflammatory adipokines in obesity-related diseases. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 25 (7): 348–355. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2014.03.009.
10. Utzeri E, Usai P (2017) Role of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on intestinal permeability and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 23 (22): 3954-3963. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3954.
11. Cipolla-Neto J, Amaral FG, Afeche SC, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2014) Melatonin, energy metabolism, and obesity: a review. J. Pineal Res. 56 (4): 371-381. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12137.
12. Reiter, RJ, Tan, D-X, Manchester, LC, Qi, W(2001) Biochemical reactivity of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 34 (2): 237-256. doi: 10.1385/CBB:34:2:237.
13. Sun H, Huang FF, Qu S (2015) Melatonin: a potential intervention for hepatic steatosis. Lipids Health Dis. 14 (1): 1-6. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0081-7.
14. Sun H, Wang X, Chen J, Song K, Gusdon AM, Li L, Bu L, Qu S (2016) Melatonin improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via MAPK-JNK/P38 signaling in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Lipids Health Dis. 15 (1): 202. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0370-9.
15. Ghosh A, Bose G, Dey T, Pal PK, Mishra S, Ghosh AK, Chattopadhyay A, Bandyopadhyay D (2019) Melatonin protects against cardiac damage induced by a combination of high fat diet and isoproterenol exacerbated oxidative stress in male Wistar rats. Melatonin Res. 2 (1): 9-31. doi: 10.32794/mr11250009.
16. Bose G, Ghosh A, Chattopadhyay A, Pal PK, Bandyopadhyay D (2019) Melatonin as a potential therapeutic molecule against myocardial damage caused by high fat diet (HFD). Melatonin Res. 2 (3): 37-56. doi: 10.32794/mr11250030.
17. Hatzis G, Ziakas P, Kavantzas N, Triantafyllou A, Sigalas P, Andreadou I, Ioannidis K, Chatzis S, Filis K, Papalampros A, Sigala F (2013). Melatonin attenuates high fat diet-induced fatty liver disease in rats. World J. Hepatol. 5 (4): 160–169. doi:10.4254/wjh.v5.i4.160.
18. Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C (2013) Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 384: 766–781.
19. Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS (2019) Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 92: 82-97. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.014.
20. Farrell GC (2003) Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: what is it, and why is it important in the Asia Pacific region? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18 (2): 124-138. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.02989.x.
21. Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS (2016) Adipokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 65 (8): 1062-1079. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.11.006.
22. Alkhouri N, Dixon LJ, Feldstein AE (2009) Lipotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: not all lipids are created equal. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 3 (4): 445–451. doi:10.1586/egh.09.32.
23. Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Lane MD, Clemens M, Diehl AM (1997) Obesity increases sensitivity to endotoxin liver injury: implications for the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94 (6): 2557-2562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2557.
24. Angulo P, Machado MV, Diehl AM (2015) Fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: mechanisms and clinical implications. Semin. Liver Dis. 35 (2): 132–145. Doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1550065.
25. Wells RG, Schwabe RF (2015) Origin and function of myofibroblasts in the liver. Semin. Liver Dis. 35 (2): 97–106. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1554915.
26. Guo J, Ren W, Li A, Ding Y, Guo W, Su D, Hu C, Xu K, Chen H, Xu X, Yang T (2013) Fat mass and obesity-associated gene enhances oxidative stress and lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 58 (4): 1004-1009. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2516-6.
27. Lazar MA (2007) Resistin- and Obesity-associated Metabolic Diseases. Horm. Metab.
Res. 39 (10): 710–716. doi:10.1055/s-2007-985897.
28. Lee H, Lee YJ, Choi H, Ko EH, Kim JW (2009) Reactive oxygen species facilitate adipocyte differentiation by accelerating mitotic clonal expansion. J. Biol. Chem. 284 (16): 10601-10609. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808742200
29. Zeyda M, Stulnig TM (2009) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance – a mini-
review. Gerontology 55 (4): 379-386. doi: 10.1159/000212758.
30. Trujillo ME, Scherer PE (2005) Adiponectin–journey from an adipocyte secretory protein biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 257 (2): 167-175. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01426.x.
31. Morton GJ, Schwartz MW (2011) Leptin and the central nervous system control of glucose metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 91: 389 – 411. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00007.2010.
32. Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P (1995) Recombinant mouse OB
protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks.
Science 269 (5223): 546 – 549. doi: 10.1126/science.7624778.
33. Vaisse C, Halaas JL, Horvath CM, Darnell JE Jr, Stoffel M, Friedman JM (1996) Leptin activation of Stat3 in the hypothalamus of wild-type and ob/ob mice but not db/db mice. Nat. Genet. 14 (1): 95 – 97. doi: 10.1038/ng0996-95.
34. Hosoi T, Kawagishi T, Okuma Y, Tanaka J, Nomura Y (2002) Brain stem is a direct
target for leptins action in the central nervous system. Endocrinology 143: 3498 – 3504. doi:10.1210/en.2002-220077.
35. Mantzoros CS, Flier JS (2000) Editorial: leptin as a therapeutic agent–trials and tribulations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85 (11): 4000 – 4002. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.11.7062.
36. Munzberg H, Myers MG Jr (2005) Molecular and anatomical determinants of central leptin resistance. Nat. Neurosci. 8 (5): 566 – 570. doi: 10.1038/nn1454.
37. Kubota N, et al. (2007) Adiponectin stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the hypothalamus and increases food intake. Cell Metab. 6 (1): 55–68. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2007.06.003.
38. Schwartz MW, Porte D Jr (2005) Diabetes, obesity, and the brain. Science 307: 375–379. doi: 10.1126/science.1104344.
39. Yang Ye A, Marumo T, Lafontan M, Busse R (1999) Leptin induces oxidative stress in human endothelial cells. FASEB J. 13 (10):1231-1238. PMID: 10385613.
40. Yamagishi SI, Edelstein D, Du XL, Kaneda Y, Guzmán M, Brownlee M (2001) Leptin induces mitochondrial superoxide production and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in aortic endothelial cells by increasing fatty acid oxidation via protein kinase A. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (27): 25096-250100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007383200.
41. Heyden MS, West AP, Ghosh S (2006) NF kappa B and immune response. Oncogene
25 (51): 6758-6780. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209943.
42. Wang Y, Ausman LM, Russell RM, Greenberg AS, Wang XD (2008) Increased apoptosis in high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats is associated with c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation and elevated proapoptotic Bax. J. Nutr. 138 (10): 1866-1871. doi:10.1093/jn/138.10.1866.
43. Abdelmegeed MA, Yoo SH, Henderson LE, Gonzalez FJ, Woodcroft KJ, Song BJ (2011) PPARalpha expression protects male mice from high fat-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver. J. Nutr. 141 (4): 603–610. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.135210.
44. Kern PA, Saghizadeh M, Ong JM, Bosch RJ, Deem R, Simsolo RB (1995) The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue: Regulation by obesity, weight loss, and relationship to lipoprotein lipase. J. Clin. Invest. 95 (5): 2111-2119. doi: 10.1172/JCI117899.
45. Gallelli L, Galasso O, Falcone D, Southworth S, Greco M, Ventura V, Romualdi P, Corigliano A, Terracciano R, Savino R, Gulletta E (2013) The effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on clinical outcomes, synovial fluid cytokine concentration and signal transduction pathways in knee osteoarthritis. A randomized open label trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21 (9): 1400-1408. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2013.06.026.
46. Bondia-Pons I, Ryan L, Martinez JA (2012) Oxidative stress and inflammation interactions in human obesity. J. Physiol. Biochem 68: 701-711. doi: 10.1007/s13105-012-0154-2.
47. Fernández-Sánchez A, Madrigal-Santillán E, Bautista M, Esquivel-Soto J, Morales-González Á, Esquivel-Chirino C, Durante-Montiel I, Sánchez-Rivera G, Valadez-Vega C, Morales-González JA (2011) Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int. J. Mo.l Sci. 12 (5): 3117-3132. doi:10.3390/ijms12053117.
48. Roberts CK, Sindhu KK (2009) Oxidative stress and metabolic syndrome. Life Sci. 84 (21-22): 705-712. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.02.026.
49. Birben E, Sahiner UM, Sackesen C, Erzurum S, Kalayci O (2012) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J. 5 (1): 9-19. doi: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e3182439613.
50. Brieger K, Schiavone S, Miller FJ Jr, Krause KH (2012) Reactive oxygen species: from health to disease. Swiss Med Wkly. 142: w13659. doi: 10.4414/smw.2012.13659.
51. Muñoz A, Costa M (2013) Nutritionally mediated oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013: 610950. doi: 10.1155/2013/610950.
52. Patti ME, Corvera S (2010) The role of mitochondria in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 31 (3): 364-395. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0027.
53. Frohnert BI, Bernlohr DA (2013) Protein carbonylation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and insulin resistance. Adv. Nutr. 4 (2): 157-163. doi: 10.3945/an.112.003319.
54. Bonnard C, Durand A, Peyrol S, Chanseaume E, Chauvin MA, Morio B, Vidal H, Rieusset J (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction results from oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118 (2): 789-800. doi: 10.1172/JCI32601.
55. Freeman LR, Zhang L, Nair A, Dasuri K, Francis J, Fernandez-Kim SO, Bruce-Keller AJ, Keller JN (2013) Obesity increases cerebrocortical reactive oxygen species and impairs brain function. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 56: 226-233. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.577.
56. Ma W, Yuan L, Yu H, Xi Y, Xiao R (2014) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in the brain of diet-induced obese rats but not in diet-resistant rats. Life Sci. 110 (2): 53- 60. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.07.018.
57. Chen JX, Stinnett A (2008) Critical role of the NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox on vascular TLR expression and neointimal lesion formation in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Lab. Invest. 88 (12): 1316-1328.
58. Marchesi C, Ebrahimian T, Angulo O, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL (2009) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling and perivascular adipose oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to vascular dysfunction in a rodent model of metabolic syndrome. Hypertension 54 (6): 1384-1392. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.138305.
59. Hernández-Aguilera A, Rull A, Rodríguez-Gallego E, Riera-Borrull M, Luciano-Mateo F, Camps J, Menéndez JA, Joven J. Mitochondrial dysfunction (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction: a basic mechanism in inflammation-related non-communicable diseases and therapeutic opportunities. Mediators Inflamm. 2013: 135698. doi: 10.1155/2013/135698.
60. Jheng HF, Huang SH, Kuo HM, Hughes MW, Tsai YS (2015) Molecular insight and pharmacological approaches targeting mitochondrial dynamics in skeletal muscle during obesity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1350: 82-94. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12863
61. de Mello AH, Costa AB, Engel JDG, Rezin GT (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life sci. 192: 26-32. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2017.11.019.
62. Vane JR (2000) The fight against rheumatism: from willow bark to COX-1 sparing drugs. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 51 (4 Pt 1): 573-586. PMID: 11192932.
63. Brater DC (1988) Clinical pharmacology of NSAIDs. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 28 (6): 518-523. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb03171.x.
64. Poddubnyy D, Song IH, Sieper J (2009) A systematic comparison of rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 27 (4 Suppl 55): S148-151. PMID: 19822063.
65. McCarberg B, Tenzer P (2013) Complexities in the pharmacologic management of osteoarthritis pain. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 29 (5): 539-548. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.785391.
66. Crofford LJ (2013) Use of NSAIDs in treating patients with arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 15: (Suppl 3): S2. doi: 10.1186/ar4174.
67. Marnett LJ (2009) The COXIB experience: A look in the rearview mirror. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 49 (1): 265-290. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145638.
68. Schoen RT, Vender RJ (1989) Mechanisms of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastric damage. Am. J. Med. 86 (4): 449–458. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(89)90344-6.
69. Laine L, Bombardier C, Hawkey CJ, Davis B, Shapiro D, Brett C, Reicin A (2002) Stratifying the risk of NSAID-related upper gastrointestinal clinical events: results of a double-blind outcomes study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Gastroenterology 123 (4):1006-1012. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.36013.
70. Mason RP, Walter MF, McNulty HP, Lockwood SF, Byun J, Day CA, Jacob RF (2006) Rofecoxib increases susceptibility of human LDL and membrane lipids to oxidative damage: a mechanism of cardiotoxicity. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 47 (1): S7-S14. doi: 10.1097/00005344-200605001-00003.
71. Bachhi S, Palumbo P, Sponta A, Coppolino MF (2012) clinical pharmacology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a review. Antiinflamm. AntiAllergy Agents Med. Chem. 11 (1): 52-64. doi:10.2174/187152312803476255.
72. Malespin MH (2018) Risk of nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs and safety of acetaminophen in patients with advanced liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. (Hoboken) 12 (3): 85-88. doi: 10.1002/cld.737.
73. Conaghan PG (2013) A turbulent decade for NSAIDs: update on current concepts ofclassification, epidemiology, comparative efficacy, and toxicity. Rheumatol. Inter. 32 (6): 1491-1502. doi:10.1007/s00296-011-2263-6.
74. Smith WL, DeWitt DL, Garavito, RM (2000) Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 69: 145-182. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.145.
75. Kraemer SA, Meade EA, DeWitt DL (1992) Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase gene structure: Identification of the transcriptional start site and 5’-flanking regulatory sequences. Arch. Biochem. Byophys. 293 (2): 391-400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90411-o.
76. Simmons DL, Botting RM, Hla T (2004) Cyclooxygenase Isozymes: The biology of Prostaglandin Synthesis and Inhibition. Pharmacol. Rev. 56 (3): 387-437. doi: 10.1124/pr.56.3.3.
77. Hernández-Díaz S, Rodríguez LA (2000) Association between nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding/perforation: An overview of epidemiologic studies published in the 1990s. Arch. Intern. Med. 160 (14): 2093-2099. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.14.2093.
78. Teoh NC, Farrell GC (2003) Hepatotoxicity associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin. Liver Dis. 7 (2): 401- 413. doi: 10.1016/s1089-3261(03)00022-9
79. Aithal, GP, Day CP (2007) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced hepatotoxicity. Clin. Liver Dis. 11 (3): 563-575. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2007.06.004.
80. Walker AM (1997) Quantitative studies of the risk of serious hepatic injury in persons using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 40 (2): 201–208. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400204.
81. Bjorkman D (1998) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated toxicity of the liver, lower gastrointestinal tract and the esophagus. Am. J. Med. 105 (5A): 17S–21S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(98)00276-9.
82. Navarro SL, Saracino MR, Makar KW, Thomas SS, Li L, Zheng Y (2011) Determinants of aspirin metabolism in healthy men and women: effects of dietary inducers of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. J. Nutrigenet. Nutrigenomics. 4 (2): 110-118. doi: 10.1159/000327782.
83. Verbeeck RK, Blackburn JL, Loewen GR (1983) Clinical pharmacokinetics of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 8 (4): 297-331. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198308040-00003.
84. Rabinovitz M, Van Thiel DH (1992) Hepatotoxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 87 (12): 1696–1704. PMID: 1449128.
85. Aithal GP, Day CP (1999). The natural history of histologically proved drug induced liver disease. Gut 44 (5): 731–735. doi:10.1136/gut.44.5.731.
86. Jones AL, Latham T, Shallcross TM, Simpson KJ (1998). Fulminant hepatic failure due to diclofenac treated successfully by orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 30 (1): 192–194. doi10.1016/s0041-1345(97)01228-1.
87. Helfgott SM, Sandberg-Cook, J, Zakim D, Nestler J. (1990). Diclofenac-associated hepatotoxicity. JAMA 264 (20): 2660–2662.
88. Kang HS, Ock J, Lee HJ, Lee YJ, Kwon BM, Hong SH (2013) Early growth response protein 1 upregulation and nuclear translocation by 2'-benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde induces prostate cancer cell death. Cancer Lett. 329 (2): 217-227. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.006.
89. Vaish V, Piplani, H, Rana C, Vaiphei K, Sanyal SN (2013) NSAIDs may regulate EGR-1-mediated induction of reactive oxygen species and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gene (NAG)-1 to initiate intrinsic pathway of apoptosis for the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 378 (1-2): 47–64. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1593-y.
90. Finkel T, Holbrook NJ (2000) Oxidants, oxidative stress, and the biology of aging. Nature 408 (6809): 239–247; 2000. doi: 10.1038/35041687.
91. Skulachev VP (1996) Role of uncoupled and noncoupled oxidations in maintenance of safely low levels of oxygen and its one-electron reductants. Q. Rev. Biophys. 29 (2): 169–202. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005795.
92. Bourdon E, Blache D (2001) The importance of proteins in defense against oxidation. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 3 (2): 293-311. doi:10.1089/152308601300185241.
93. Zhang Y, Marcillat O, Giulivi C, Ernster L, Davies KJ (1990) The oxidative inactivation of mitochondrial electron transport chain components and ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 265 (27): 16330–16336. PMID: 2168888.
94. Macsween RN, Burt AD (1986) Histologic spectrum of alcoholic liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 6 (3): 221–232. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040605.
95. Lieber CS (2000) Alcoholic liver disease: new insights in pathogenesis lead to new treatments. J. Hepatol. 32 (1): 113–128. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(00)80420-1.
96. Crabb DW (1995) Ethanol oxidizing enzymes: roles in alcohol metabolism and alcoholic liver disease. Prog. Liver Dis. 13: 151–172. PMID: 9224501.
97. Kamimura S, Gaal K, Britton RS, Bacon BR, Triadafilopoulos G, Tsukamoto H (1992) Increased 4-hydroxynonenal levels in experimental alcoholic liver disease: association of lipid peroxidation with liver fibrogenesis. Hepatology 16 (2): 448–453. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160225.
98. Bedossa P, Houglum K, Trautwein C, Holstege A, Alcorn J, Chojkier M (1994) Stimulation of collagen a1 gene expression is associated with lipid peroxidation in hepatocellular injury: a link to tissue fibrosis? Hepatology 19 (5): 1262–1271. PMID: 8175151.
99. Seki S, Kitada T, Yamada T, Sakaguchi H, Nakatani K, Wakasa K (2002) In situ detection of lipid peroxidation and oxidative DNA damage in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 37 (1): 56-62. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00073-9.
100. Koruk M, Taysi S, Savas MC, Yilmaz O, Akcay F, Karakok M (2004). Oxidative stress and enzymatic antioxidant status in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 34 (1): 57–62. PMID: 15038668.
101. Videla LA, Rodrigo R, Orellana M, Fernandez V, Tapia G, Quiñones L, Varela N, Contreras J, Lazarte R, Csendes A, Rojas J, Maluenda F, Burdiles P, Diaz JC, Smok G, Thielemann L, Poniachik J (2004). Oxidative stressrelated parameters in the liver of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Clin. Sci. (Lond). 106 (3): 261–268.doi: 10.1042/CS20030285.
102. Zhang HM, Zhang Y (2014) Melatonin: a well‐documented antioxidant with conditional pro‐oxidant actions. J. Pineal res. 57 (2): 131-46. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12162.
103. Sandoval-Acuña C, Lopez-Alarcón C, Aliaga ME, Speisky H (2012) Inhibition of mitochondrial complex I by various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and its protection by quercetin via a coenzyme Q-like action. Chem. Biol. Interact. 199 (1): 18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.05.006.
104. Masubuchi Y, Nakayama S, Horie T (2002) Role of mitochondrial permeability transition in diclofenac-induced hepatocyte injury in rats. Hepatology 35 (3): 544-551. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31871.
105. Bort R, Ponsoda X, Jover R, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Castell JV (1999) Diclofenac toxicity to hepatocytes: a role for drug metabolism in cell toxicity. J. Pharmacol Exp. Ther. 288 (1): 65-72. PMID: 9862754.
106. Masubuchi Y, Yamada S, Horie T (2000). Possible mechanisms of hepatocyte injury induced by diphenylamine and its structurally related NSAIDS. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292 (3): 982–987. PMID: 10688613.
107. Kantrow SP, Piantadosi CA (1997) Release of cytochrome c from liver mitochondria during permeability transition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 232 (3): 669–671. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6353.
108. Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler M, Larochette N, Goodlett DR, Aebersold R, Siderovski DP, Penninger JM, Kroemer G (1999) Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 397 (6718): 441-446. doi: 10.1038/17135.
109. Javadov S, Karmazyn M (2007) Cellular physiology biochemistry and biochemistry mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening as an endpoint to initiate cell death and as a putative target for cardioprotection. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 20 (1-4): 1–22. doi:10.1159/000103747.
110. Souto EO, Miyoshi H, Dubois RN, Gores GJ (2001) Kupffer cell derived cyclooxygenase-2 regulates hepatic Bcl-2 expression in choledocho-venus fistula rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 280 (5): G805-G811. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2001.280.5.G805.
111. Lerner AB, Case JD, Takahashi Y, Lee TH, Mori W (1958) Isolation of melatonin, the pineal gland factor that lightens melanocytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80: 2587–2589.doi:10.1021/ja01543a060.
112. Axelrod J. Weissbach H (1960) Enzymatic O-methylation of N-acetylserotonin to melatonin. Science 131 (3409): 1312 doi: 10.1126/science.131.3409.1312.
113. Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Collin, F (2010) Melatonin: Action as antioxidant and potential applications in human disease and aging. Toxicology 278 (1): 55–67. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2010.04.008.
114. Kvetnoy IM (1999) Extrapineal melatonin: location and role within diffuse neuroendocrine system. Histochem. J. 31 (1): 1-12. doi: 10.1023/a:1003431122334.
115. Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral S, Tan DX, Jou MJ, Galano A, Xu B (2017) Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant: one of evolution’s best ideas. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 74 (21): 3863–3881. doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2609-7.
116. Rinella ME (2015) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. JAMA 313 (22): 2263–2273. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.5370.
117. Williams CD, Stengel J, Asike MI, Torres DM, Shaw J, Contreras M, Landt CL, Harrison SA (2011) Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study. Gastroenterology 140 (1): 124–131. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.09.038.
118. Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Stern N, Bilu C, El-Osta A, Einat H, Kronfeld-Schor N (2019) The Circadian Syndrome: is the Metabolic Syndrome and much more! J. Intern. Med. 286 (2): 181-191. doi: 10.1111/joim.12924.
119. Cardinali DP, Hardeland R (2017) Inflammaging, metabolic syndrome and melatonin: A call for treatment studies. Neuroendocrinology 104 (4): 382–397. doi:10.1159/000446543.
120. Yu JS, Marsh S, Hu JB, Feng WK, Wu CD (2016) The pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and genetic background. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016: 2862173. Doi:10.1155/2016/2862173.
121. Reinke H, Asher G (2016) Circadian clock control of liver metabolic functions. Gastroenterology 150 (3): 574-580. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.11.043.
122. Rodriguez C, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Antolín I, Herrera F, Martín V, Reiter RJ (2004) Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: a significant role for melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 36 (1): 1-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1600-079x.2003.00092.x.
123. Tomás-Zapico C, Coto-Montes A (2005) A proposed mechanism to explain the stimulatory effect of melatonin on antioxidative enzymes. J. Pineal Res. 39 (2): 99-104. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00248.x.
124. Oleshchuk O, Ivankiv Y, Falfushynska H, Mudra A, Lisnychuk N (2019) Hepatoprotective effect of melatonin in toxic liver injury in rats. Medicina (Kaunas). 55 (6): 304. doi: 10.3390/medicina55060304.
125. Pan M, Song YL, Xu JM, Gan HZ (2006) Melatonin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver induced by high-fat diet in rats. J. Pineal Res. 41 (1): 79-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00346.x.
126. Sewerynek E, Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D, Ortiz GG, Lewinski A (1996) Oxidative damage in the liver induced by ischemia-reperfusion: protection by melatonin. Hepato-gastroenterology 43 (10): 898–905.
127. Zaitone S, Hassan N, El-Orabi N, El-Awady el-S (2011) Pentoxifylline and melatonin in combination with pioglitazone ameliorate experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 662 (1-3): 70-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.04.049.
128. Pakravan H, Ahmadian M, Fani A, Aghaee D, Brumanad S, Pakzad B (2017) The effects of melatonin in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Adv. Biomed. Res. 6: 40. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.204593.
129. Mularczyk A, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ (2012) The effects of long-term melatonin treatment on plasma liver enzymes levels and plasma concentrations of lipids and melatonin in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 63 (1): 35-40. PMID: 22460459.
130. Garbers C, Aparicio-Siegmund S, Rose-John S (2015). The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: recent advances towards specific inhibition. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 34: 75–82. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2015.02.008.
131. Song Z, Humar B, Gupta A, Maurizio E, Borgeaud N, Graf R, Clavien PA, Tian Y (2018) Exogenous melatonin protects small-for-size liver grafts by promoting monocyte infiltration and releases interleukin-6. J. Pineal Res. 65 (1): e12486. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12486.
132. Day CP, James OF (1998) Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”?. Gastroenterology 114 (4): 842-845. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70599-2.
133. Shah SA, Khan M, Jo MH, Jo MG, Amin FU, Kim MO (2017). Melatonin stimulates the sirt1/nrf2 signaling pathway counteracting lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress to rescue postnatal rat brain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 23 (1): 33–44. doi:10.1111/cns.12588.
134. Chuang JI, Mohan N, Meltz ML, Reiter RJ (1996) Effect of melatonin of NF-kB DNA-binding activity in rat spleen. Cell Biol. Int. 20 (1): 687-692. doi: 10.1006/cbir.1996.0091.
135. Bertuglia S, Marchiafava PL, Colantuoni A (1996) Melatonin prevents ischemia reperfusion injury in the hamster cheek pouch. Cardiovasc. Res. 31 (6): 947-952. PMID: 8759251.
136. Stacchiotti A, Favero G, Lavazza A, Golic I, Aleksic M, Korac A, Rodella LF, Rezzani R (2016) Hepatic macrosteatosis is partially converted to microsteatosis by melatonin supplementation in ob/ob mice non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PloS One 11 (1): e0148115. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0148115.
137. Kim JA, Wei Y, Sowers JR (2008) Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in insulin resistance. Circ. Res. 102 (4): 401-14. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.165472.
138. Vial G, Dubouchaud H, Leverve XM (2010) Liver mitochondria and insulin resistance. Acta Biochim. Pol. 57 (4): 389-92. Epub 2010 Nov 16. PMID: 21079817.
139. Pérez-Carreras M, Del Hoyo P, Martín MA, Rubio JC, Martín A, Castellano G, Colina F, Arenas J, Solis-Herruzo JA (2003) Defective hepatic mitochondrial respiratory chain in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 38 (4): 999-1007. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50398.
140. Dey A, Swaminathan K (2010) Hyperglycemia-induced mitochondrial alterations in liver. Life Sci. 87 (7-8): 197-214. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.06.007.
141. Schrauwen P (2007) Of the fit and the fat: mitochondrial abnormalities and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92: 1229–1231. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0295.
142. Escames G, Acuña-Castroviejo D, López LC, Tan DX, Maldonado MD, Sánchez-Hidalgo M, León J, Reiter RJ (2006) Pharmacological utility of melatonin in the treatment of septic shock: experimental and clinical evidence. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 58 (9): 1153-65. doi: 10.1211/jpp.58.9.0001.
143. Tan DX, Manchester LC, Liu X, Rosales-Corral SA, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Reiter RJ (2013) Mitochondria and chloroplasts as the original sites of melatonin synthesis: a hypothesis related to melatonin's primary function and evolution in eukaryotes. J. Pineal Res. 54 (2):127-38. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12026.
144. Tan DX, Manchester LC, Qin L, Reiter RJ (2016) Melatonin: A mitochondrial targeting molecule involving mitochondrial protection and dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17 (12): 2124. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122124.
145. Agil A, El-Hammadi M, Jiménez-Aranda A, Tassi M, Abdo W, Fernández-Vázquez G, Reiter RJ (2015) Melatonin reduces hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic obese rats. J. Pineal Res. 59 (1): 70–79. doi:10.1111/jpi.12241.
146. Martín M, Macías M, Escames G, Reiter RJ, Agapito MT, Ortiz GG, Acuña-Castroviejo D (2000) Melatonin-induced increased activity of the respiratory chain complexes I and IV can prevent mitochondrial damage induced by ruthenium red in vivo. J. Pineal Res. 28 (4): 242-8. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-079x.2000.280407.x.
147. Martín M, Macías M, León J, Escames G, Khaldy H, Acuña-Castroviejo D (2002) Melatonin increases the activity of the oxidative phosphorylation enzymes and the production of ATP in rat brain and liver mitochondria. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34 (4): 348-357. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(01)00138-8.
148. Acuña-Castroviejo D, Martín M, Macías M, Escames G, León J, Khaldy H, Reiter RJ (2001) Melatonin, mitochondria, and cellular bioenergetics. J. Pineal Res. 30 (2): 65-74. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-079x.2001.300201.x.
149. Reiter RJ (2000) Melatonin: Lowering the high price of free radicals. News Physiol. Sci. 15: 246-250. doi: 10.1152/physiologyonline.2000.15.5.246.
150. de Atenor MS, de Romero IR, Brauckmann E, Pisanó A, Legname AH (1994) Effects of the pineal gland and melatonin on the metabolism of oocytes in vitro and on ovulation in Bufo arenarum. J. Exp. Zool. 268 (6): 436-41. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402680604.
151. Reyes-Toso CF, Ricci CR, de Mignone IR, Reyes P, Linares LM, Albornoz LE, Cardinali DP, Zaninovich A (2003) In vitro effect of melatonin on oxygen consumption in liver mitochondria of rats. Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 24 (5): 341-4. PMID: 14647009.
152. Reyes-Toso CF, Rebagliati IR, Ricci CR, Linares LM, Albornoz LE, Cardinali DP, Zaninovich A (2006) Effect of melatonin treatment on oxygen consumption by rat liver mitochondria. Amino. Acids 31 (3): 299-302. doi: 10.1007/s00726-005-0280-z.
153. Radogna F, Diederich M, Ghibelli L (2010) Melatonin: a pleiotropic molecule regulating inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 80 (12): 1844-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.07.041.
154. Mularczyk A, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ (2012) The effects of long-term melatonin treatment on plasma liver enzymes levels and plasma concentrations of lipids and melatonin in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. J. Physiol Pharmacol. 63 (1): 35-40. PMID: 22460459.
155. Flower RJ, Vane JR (1972) Inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase in brain explains the anti-pyretic activity of paracetamol (4-acetamidophenol). Nature 240 (5831): 410-411. doi: 10.1038/240410a0.
156. Vane JR (1971) Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat. New Biol. 231 (25): 232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0.
157. Murphy PJ, Badia P, Myers BL, Boecker MR, Wright KP Jr (1994) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs affect normal sleep patterns in humans. Physiol. Behav. 55 (6): 1063–1066. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(94)90388-3.
158. Hayaishi O (1991) molecular mechanisms of sleep-wake regulation: Roles of prostaglandin D2s and E2. FASEB J. 5 (11): 2575-2581;1991. doi:10.1096/fasebj.5.11.1907936.
159. Kang P, Dalvie D, Smith E, Renner M (2009) Bioactivation of Lumiracoxib by peroxidases and human liver microsomes: identification of multiple quinone imine intermediates and GSH adducts. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 22 (1): 106-117. doi: 10.1021/tx8002356.
160. Karakilcik AZ, Bitiren M, Zerin M, Celik H, Aksoy N (2015) Melatonin increased vitamin C and antioxidant enzyme values in the plasma, heart, liver, and kidney of adriamycin-treated rats. Turk. J. Biol. 39 (6): 925–931. doi:10.3906/biy-15077.
161. Kesh SB, Sarkar DE, Manna KR (2016) High-fat diet-induced oxidative stress and its impact on metabolic syndrome: a review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 9 (1): 47-52.
162. Magliano M (2008) Obesity and arthritis. Menopause International. 14 (4): 149–154. doi:10.1258/mi.2008.008018.
163. O'Connor N, Dargan PI, Jones AL (2003) Hepatocellular damage from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. QJM 96 (11): 787-91. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcg138.
164. Cho JH, Bhutani S, Kim CH, Irwin MR (2021) Anti-inflammatory effects of melatonin: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Brain. Behavior. Immunity 93: 245–253. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2021.01.034.
165. Bahinipati J, Sarangi R, Pathak M, Mohapatra S (2022) Effect of night shift on development of metabolic syndrome among health care workers. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 11 (5): 1710-1715. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_375_21.
166. Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2011) Melatonin as a natural ally against oxidative stress: a physicochemical examination. J. Pineal Res. 51: 1-16. DOI: 10.1111/ј.1600-079X.2011.00916.x.
167. Cardinali DP, Golombek DA, Rosenstein RE, Cutrera RA, Esquifino AI (1997) Melatonin site and mechanism of action: single or multiple? J. Pineal Res. 23: 32-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.1997.tb00332.x.
168. Li Y, Ma J, Yao K, Su W, Tan B, Wu X, Huang X, Li T, Yin Y, Tosini G, Yin J (2020) Circadian rhythms and obesity: Timekeeping governs lipid metabolism. J. Pineal Res. 69 (3): e12682. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12682.
169. Agil A, Rosado I, Ruiz R, Figueroa A, Zen N, Fernández-Vázquez G (2012) Melatonin improves glucose homeostasis in young Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J. Pineal Res. 52 (2): 203-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00928.x.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


