Role of melatonin in regulating neurogenesis: Implications for the neurodegenerative pathology and analogous therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease
Melatonin in regulating neurogenesis
Abstract
The revelation of adult brain exhibiting neurogenesis has established that the brain possesses great plasticity and that neurons could be spawned in the neurogenic zones where hippocampal adult neurogenesis attributes to learning and memory processes. With strong implications in brain functional homeostasis, aging and cognition, various aspects of adult neurogenesis reveal exuberant mechanistic associations thereby further aiding in facilitating the therapeutic approaches regarding the development of neurodegenerative processes in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). Impaired neurogenesis has been significantly evident in AD with compromised hippocampal function and cognitive deficits. Melatonin the pineal indolamine augments neurogenesis and has been linked to AD development as its levels are compromised with disease progression. Here, in this review, we discuss and appraise the mechanisms via which melatonin regulates neurogenesis in pathophysiological conditions which would unravel the molecular basis in such conditions and its role in endogenous brain repair. Also, its components as key regulators of neural stem and progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation in the embryonic and adult brain would aid in accentuating the therapeutic implications of this indoleamine in line of prevention and treatment of AD.
References
2. Demars MP, Hollands C, Zhao Kda T, Lazarov O (2013) Soluble amyloid precursor protein-alpha rescues age-linked decline in neural progenitor cell proliferation. Neurobiol. Aging 34: 2431-2440. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.04.016.
3. Walsh CE,Hitchcock PF (2017) Progranulin regulates neurogenesis in the developing vertebrate retina. Dev. Neurobiol. 77: 1114-1129. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22499.
4. Moreno-Jimenez EP, Flor-Garcia M, Terreros-Roncal J, Rabano A, Cafini F, Pallas-Bazarra N, Avila J, Llorens-Martin M (2019) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Nat. Med. 25: 554-560. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0375-9.
5. Hollands C, Bartolotti N, Lazarov O (2016) Alzheimer's disease and hippocampal adult neurogenesis; exploring shared mechanisms. Front. Neurosci. 10: 178. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00178.
6. Chern CM, Liao JF, Wang YH, Shen YC (2012) Melatonin ameliorates neural function by promoting endogenous neurogenesis through the MT2 melatonin receptor in ischemic-stroke mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 52: 1634-1647. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.01.030.
7. Hossain MF, Uddin MS, Uddin GMS, Sumsuzzman DM, Islam MS, Barreto GE, Mathew B, Ashraf GM (2019) Melatonin in Alzheimer's disease: A latent endogenous regulator of neurogenesis to mitigate Alzheimer's neuropathology. Mol. Neurobiol. 56: 8255-8276. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01660-3.
8. El-Sherif Y, Tesoriero J, Hogan MV, Wieraszko A (2003) Melatonin regulates neuronal plasticity in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 72: 454-460. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10605.
9. Ramirez-Rodriguez GB, Olvera-Hernandez S, Vega-Rivera NM, Ortiz-Lopez L (2018) Melatonin Influences Structural Plasticity in the Axons of Granule Cells in the Dentate Gyrus of Balb/C Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20: doi: 10.3390/ijms20010073.
10. Toda T,Gage FH (2018) Review: adult neurogenesis contributes to hippocampal plasticity. Cell Tissue Res. 373: 693-709. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2735-4.
11. Ortiz-Lopez L, Perez-Beltran C, Ramirez-Rodriguez G (2016) Chronic administration of a melatonin membrane receptor antagonist, luzindole, affects hippocampal neurogenesis without changes in hopelessness-like behavior in adult mice. Neuropharmacology 103: 211-221. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.11.030.
12. Ng KY, Leong MK, Liang H, Paxinos G (2017) Melatonin receptors: distribution in mammalian brain and their respective putative functions. Brain Struct. Funct. 222: 2921-2939. doi: 10.1007/s00429-017-1439-6.
13. Motta-Teixeira LC, Machado-Nils AV, Battagello DS, Diniz GB, Andrade-Silva J, Silva S, Jr., Matos RA, do Amaral FG, Xavier GF, Bittencourt JC, Reiter RJ, Lucassen PJ, Korosi A, Cipolla-Neto J (2018) The absence of maternal pineal melatonin rhythm during pregnancy and lactation impairs offspring physical growth, neurodevelopment, and behavior. Horm. Behav. 105: 146-156. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2018.08.006.
14. Sarlak G, Jenwitheesuk A, Chetsawang B, Govitrapong P (2013) Effects of melatonin on nervous system aging: neurogenesis and neurodegeneration. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 123: 9-24. doi: 10.1254/jphs.13r01sr.
15. Salehi M, Naseri-Nosar M, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Nourani M, Khojasteh A, Farzamfar S, Mansouri K, Ai J (2018) Polyurethane/gelatin nanofibrils neural guidance conduit containing platelet-rich plasma and melatonin for transplantation of schwann cells. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 38: 703-713. doi: 10.1007/s10571-017-0535-8.
16. Shukla M, Govitrapong P, Boontem P, Reiter RJ, Satayavivad J (2017) Mechanisms of melatonin in alleviating Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 15: 1010-1031. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170313123454.
17. Sotthibundhu A, Phansuwan-Pujito P, Govitrapong P (2010) Melatonin increases proliferation of cultured neural stem cells obtained from adult mouse subventricular zone. J. Pineal Res. 49: 291-300. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00794.x.
18. Sotthibundhu A, Ekthuwapranee K, Govitrapong P (2016) Comparison of melatonin with growth factors in promoting precursor cells proliferation in adult mouse subventricular zone. EXCLI J. 15: 829-841. doi: 10.17179/excli2016-606.
19. Tocharus C, Puriboriboon Y, Junmanee T, Tocharus J, Ekthuwapranee K, Govitrapong P (2014) Melatonin enhances adult rat hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation via ERK signaling pathway through melatonin receptor. Neuroscience 275: 314-321. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.06.026.
20. Shukla M, Chinchalongporn V, Govitrapong P, Reiter RJ (2019) The role of melatonin in targeting cell signaling pathways in neurodegeneration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1443: 75-96. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14005.
21. Song J (2019) Pineal gland dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: relationship with the immune-pineal axis, sleep disturbance, and neurogenesis. Mol. Neurodegener. 14: 28. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0330-8.
22. Daulatzai MA (2016) Pharmacotherpy and Alzheimer's Disease: The M-drugs (melatonin, minocycline, modafinil, and memantine) approach. Curr. Pharm. Des. 22: 2411-2430. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160203142111.
23. Altman J (1962) Are new neurons formed in the brains of adult mammals? Science 135: 1127-1128. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3509.1127.
24. Altman J,Das GD (1965) Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 124: 319-335. doi: 10.1002/cne.901240303.
25. Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 4: 1313-1317. doi: 10.1038/3305.
26. Kempermann G (2002) Why new neurons? Possible functions for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 22: 635-638.
27. Ming GL,Song H (2005) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 28: 223-250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.28.051804.101459.
28. Ming GL,Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70: 687-702. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.001.
29. Meerlo P, Mistlberger RE, Jacobs BL, Heller HC, McGinty D (2009) New neurons in the adult brain: the role of sleep and consequences of sleep loss. Sleep Med. Rev. 13: 187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2008.07.004.
30. Goncalves JT, Schafer ST, Gage FH (2016) Adult Neurogenesis in the hippocampus: from stem cells to behavior. Cell 167: 897-914. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.021.
31. Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Huttner HB, Bostrom E, Westerlund I, Vial C, Buchholz BA, Possnert G, Mash DC, Druid H, Frisen J (2013) Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell 153: 1219-1227. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.002.
32. Kong X, Li X, Cai Z, Yang N, Liu Y, Shu J, Pan L, Zuo P (2008) Melatonin regulates the viability and differentiation of rat midbrain neural stem cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 28: 569-579. doi: 10.1007/s10571-007-9212-7.
33. Niles LP, Armstrong KJ, Rincon Castro LM, Dao CV, Sharma R, McMillan CR, Doering LC, Kirkham DL (2004) Neural stem cells express melatonin receptors and neurotrophic factors: colocalization of the MT1 receptor with neuronal and glial markers. BMC Neurosci. 5: 41. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-5-41.
34. Sharma R, Ottenhof T, Rzeczkowska PA, Niles LP (2008) Epigenetic targets for melatonin: induction of histone H3 hyperacetylation and gene expression in C17.2 neural stem cells. J. Pineal Res. 45: 277-284. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00587.x.
35. Chen X, Li X, Du Z, Shi W, Yao Y, Wang C, He K, Hao A (2014) Melatonin promotes the acquisition of neural identity through extracellular-signal-regulated kinases 1/2 activation. J. Pineal Res. 57: 168-176. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12153.
36. Moriya T, Horie N, Mitome M, Shinohara K (2007) Melatonin influences the proliferative and differentiative activity of neural stem cells. J. Pineal Res. 42: 411-418. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00435.x.
37. Kim MJ, Kim HK, Kim BS, Yim SV (2004) Melatonin increases cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of maternally separated rats. J. Pineal Res. 37: 193-197. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2004.00157.x.
38. Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Klempin F, Babu H, Benitez-King G, Kempermann G (2009) Melatonin modulates cell survival of new neurons in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 2180-2191. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.46.
39. Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Vega-Rivera NM, Benitez-King G, Castro-Garcia M, Ortiz-Lopez L (2012) Melatonin supplementation delays the decline of adult hippocampal neurogenesis during normal aging of mice. Neurosci. Lett. 530: 53-58. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.09.045.
40. Dominguez-Alonso A, Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Benitez-King G (2012) Melatonin increases dendritogenesis in the hilus of hippocampal organotypic cultures. J. Pineal Res. 52: 427-436. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00957.x.
41. Chu J, Tu Y, Chen J, Tan D, Liu X, Pi R (2016) Effects of melatonin and its analogues on neural stem cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 420: 169-179. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.10.012.
42. Mendivil-Perez M, Soto-Mercado V, Guerra-Librero A, Fernandez-Gil BI, Florido J, Shen YQ, Tejada MA, Capilla-Gonzalez V, Rusanova I, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Lopez LC, Velez-Pardo C, Jimenez-Del-Rio M, Ferrer JM, Escames G (2017) Melatonin enhances neural stem cell differentiation and engraftment by increasing mitochondrial function. J. Pineal Res. 63: e12415. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12415.
43. Liu Y, Zhang Z, Lv Q, Chen X, Deng W, Shi K, Pan L (2016) Effects and mechanisms of melatonin on the proliferation and neural differentiation of PC12 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 478: 540-545. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.093.
44. Takahashi K,Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126: 663-676. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024.
45. Takahashi K,Yamanaka S (2016) A decade of transcription factor-mediated reprogramming to pluripotency. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 17: 183-193. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.8.
46. Song J, Kang SM, Lee KM, Lee JE (2015) The protective effect of melatonin on neural stem cell against LPS-induced inflammation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015: 854359. doi: 10.1155/2015/854359.
47. Gao S, Wang ZL, Di KQ, Chang G, Tao L, An L, Wu FJ, Xu JQ, Liu YW, Wu ZH, Li XY, Gao S, Tian JH (2013) Melatonin improves the reprogramming efficiency of murine-induced pluripotent stem cells using a secondary inducible system. J. Pineal Res. 55: 31-39. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12047.
48. Bai C, Li X, Gao Y, Yuan Z, Hu P, Wang H, Liu C, Guan W, Ma Y (2016) Melatonin improves reprogramming efficiency and proliferation of bovine-induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Pineal Res. 61: 154-167. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12334.
49. Shu T, Wu T, Pang M, Liu C, Wang X, Wang J, Liu B, Rong L (2016) Effects and mechanisms of melatonin on neural differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 474: 566-571. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.04.108.
50. Bordey A (2014) Endogenous stem cells for enhancing cognition in the diseased brain. Front. Neurosci. 8: 98. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00098.
51. Lepousez G, Valley MT, Lledo PM (2013) The impact of adult neurogenesis on olfactory bulb circuits and computations. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 75: 339-363. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183731.
52. Aimone JB, Li Y, Lee SW, Clemenson GD, Deng W, Gage FH (2014) Regulation and function of adult neurogenesis: from genes to cognition. Physiol. Rev. 94: 991-1026. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00004.2014.
53. Hardeland R (2013) Melatonin and the theories of aging: a critical appraisal of melatonin's role in antiaging mechanisms. J. Pineal Res. 55: 325-356. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12090.
54. Soto-Vazquez R, Labastida-Lopez C, Romero-Castello S, Benitez-King G, Parra-Cervantes P (2016) Stimulation of dendrogenesis and neural maturation in adult mammals. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 5: 183-193. doi: 10.4155/ppa.15.43.
55. Herrera-Arozamena C, Marti-Mari O, Estrada M, de la Fuente Revenga M, Rodriguez-Franco MI (2016) Recent advances in neurogenic small molecules as innovative treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. molecules 21: 1165. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091165.
56. Yu X, Li Z, Zheng H, Ho J, Chan MT, Wu WK (2017) Protective roles of melatonin in central nervous system diseases by regulation of neural stem cells. Cell Prolif. 50: e12323. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12323.
57. Stoll EA, Habibi BA, Mikheev AM, Lasiene J, Massey SC, Swanson KR, Rostomily RC, Horner PJ (2011) Increased re-entry into cell cycle mitigates age-related neurogenic decline in the murine subventricular zone. Stem Cells 29: 2005-2017. doi: 10.1002/stem.747.
58. Apple DM, Solano-Fonseca R, Kokovay E (2017) Neurogenesis in the aging brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 141: 77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.06.116.
59. Katsimpardi L,Lledo PM (2018) Regulation of neurogenesis in the adult and aging brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 53: 131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.07.006.
60. Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Gomez-Sanchez A, Ortiz-Lopez L (2014) Melatonin maintains calcium-binding calretinin-positive neurons in the dentate gyrus during aging of Balb/C mice. Exp. Gerontol. 60: 147-152. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2014.10.014.
61. Kireev RA, Cuesta S, Vara E, Tresguerres JA (2011) Effect of growth hormone and melatonin on the brain: from molecular mechanisms to structural changes. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 7: 337-350. doi: 10.1515/HMBCI.2011.115.
62. Kireev RA, Vara E, Tresguerres JA (2013) Growth hormone and melatonin prevent age-related alteration in apoptosis processes in the dentate gyrus of male rats. Biogerontology 14: 431-442. doi: 10.1007/s10522-013-9443-6.
63. Waller KL, Mortensen EL, Avlund K, Fagerlund B, Lauritzen M, Gammeltoft S, Jennum P (2016) Melatonin and cortisol profiles in late midlife and their association with age-related changes in cognition. Nat. Sci. Sleep 8: 47-53. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S75946.
64. Venegas C, Garcia JA, Escames G, Ortiz F, Lopez A, Doerrier C, Garcia-Corzo L, Lopez LC, Reiter RJ, Acuna-Castroviejo D (2012) Extrapineal melatonin: analysis of its subcellular distribution and daily fluctuations. J. Pineal Res. 52: 217-227. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00931.x.
65. Iggena D, Winter Y, Steiner B (2017) Melatonin restores hippocampal neural precursor cell proliferation and prevents cognitive deficits induced by jet lag simulation in adult mice. J. Pineal Res. 62: e12397. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12397.
66. Lopez-Armas G, Flores-Soto ME, Chaparro-Huerta V, Jave-Suarez LF, Soto-Rodriguez S, Rusanova I, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Gonzalez-Perez O, Gonzalez-Castaneda RE (2016) Prophylactic role of oral melatonin administration on neurogenesis in adult Balb/C mice during REM sleep deprivation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016: 2136902. doi: 10.1155/2016/2136902.
67. Lopez-Virgen V, Zarate-Lopez D, Adirsch FL, Collas-Aguilar J, Gonzalez-Perez O (2015) Effects of sleep deprivation in hippocampal neurogenesis. Gac. Med. Mex. 151: 99-104.
68. Kuhn HG, Biebl M, Wilhelm D, Li M, Friedlander RM, Winkler J (2005) Increased generation of granule cells in adult Bcl-2-overexpressing mice: a role for cell death during continued hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 22: 1907-1915. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04377.x.
69. Hinojosa-Godinez A, Jave-Suarez LF, Flores-Soto M, Galvez-Contreras AY, Luquin S, Oregon-Romero E, Gonzalez-Perez O, Gonzalez-Castaneda RE (2019) Melatonin modifies SOX2(+) cell proliferation in dentate gyrus and modulates SIRT1 and MECP2 in long-term sleep deprivation. Neural Regener. Res. 14: 1787-1795. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.257537.
70. Gao C, Wang Q, Chung SK, Shen J (2017) Crosstalk of metabolic factors and neurogenic signaling in adult neurogenesis: Implication of metabolic regulation for mental and neurological diseases. Neurochem. Int. 106: 24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.02.001.
71. Ziegler AN, Levison SW, Wood TL (2015) Insulin and IGF receptor signalling in neural-stem-cell homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11: 161-170. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.208.
72. Sun P, Hua Q, Schmitt AG (2016) Energy metabolism, adult neurogenesis and their possible roles in Alzheimer's disease: a brief overview. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 16: 493-502. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150813142611.
73. Dorsemans AC, Couret D, Hoarau A, Meilhac O, Lefebvre d'Hellencourt C, Diotel N (2017) Diabetes, adult neurogenesis and brain remodeling: New insights from rodent and zebrafish models. Neurogenesis (Austin) 4: e1281862. doi: 10.1080/23262133.2017.1281862.
74. Velazquez R, Tran A, Ishimwe E, Denner L, Dave N, Oddo S, Dineley KT (2017) Central insulin dysregulation and energy dyshomeostasis in two mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 58: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.06.003.
75. Frazier HN, Ghoweri AO, Anderson KL, Lin RL, Porter NM, Thibault O (2019) Broadening the definition of brain insulin resistance in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Exp. Neurol. 313: 79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.12.007.
76. Gurel-Gokmen B, Ipekci H, Oktay S, Alev B, Ustundag UV, Ak E, Akakin D, Sener G, Emekli-Alturfan E, Yarat A, Tunali-Akbay T (2018) Melatonin improves hyperglycemia induced damages in rat brain. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 34: e3060. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3060.
77. Owino S, Contreras-Alcantara S, Baba K, Tosini G (2016) Melatonin signaling controls the daily rhythm in blood glucose levels independent of peripheral clocks. PLoS One 11: e0148214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148214.
78. Owino S, Buonfiglio DDC, Tchio C, Tosini G (2019) Melatonin signaling a key regulator of glucose homeostasis and energy metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 10: 488. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00488.
79. Tiong YL, Ng KY, Koh RY, Ponnudurai G, Chye SM (2019) Melatonin prevents oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in high glucose-treated schwann cells via upregulation of Bcl2, NF-kappaB, mTOR, Wnt signalling pathways. Antioxidants (Basel) 8: 198. doi: 10.3390/antiox8070198.
80. Xu J, Gao H, Zhang L, Rong S, Yang W, Ma C, Chen M, Huang Q, Deng Q, Huang F (2019) Melatonin alleviates cognition impairment by antagonizing brain insulin resistance in aged rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Pineal Res. 67: e12584. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12584.
81. Lyssenko V, Nagorny CL, Erdos MR, Wierup N, Jonsson A, Spégel P, Bugliani M, Saxena R, Fex M, Pulizzi N, Isomaa B, Tuomi T, Nilsson P, Kuusisto J, Tuomilehto J, Boehnke M, Altshuler D, Sundler F, Eriksson JG, Jackson AU, Laakso M, Marchetti P, Watanabe RM, Mulder H, Groop L (2009) Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion. Nat. Genet. 41: 82-88. doi:10.1038/ng.288.
82. McMullan CJ, Curhan GC, Schernhammer ES, Forman JP (2013) Association of nocturnal melatonin secretion with insulin resistance in nondiabetic young women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 178: 231-238. doi:10.1093/aje/kws470.
83. Rubio-Sastre P, Scheer FA, Gómez-Abellán P, Madrid JA, Garaulet M (2014) Acute melatonin administration in humans impairs glucose tolerance in both the morning and evening. Sleep 37: 1715-1719. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4088
84. Jia G, Gao Y, Li C, Zhang Y (2020) Effects of MTNR1B genetic variants on individual susceptibility to gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Perinatol. 37: 607-612. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1685446.
85. Tuomi T, Nagorny CLF, Singh P, Bennet H, Yu Q, Alenkvist I, Isomaa B, Östman B, Söderström J, Pesonen AK, Martikainen S, Räikkönen K, Forsén T, Hakaste L, Almgren P, Storm P, Asplund O, Shcherbina L, Fex M, Fadista J, Tengholm A, Wierup N, Groop L, Mulder H (2016) Increased melatonin signaling is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 23: 1067-1077. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.009.
86. Li H, Zhang Y, Liu S, Li F, Wang B, Wang J, Cao L, Xia T, Yao Q, Chen H, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Li Y, Li G, Wang J, Li X, Ni S (2019) Melatonin enhances proliferation and modulates differentiation of neural stem cells via autophagy in hyperglycemia. Stem Cells 37: 504-515. doi: 10.1002/stem.2968.
87. Kadry SM, El-Dakdoky MH, Haggag NZ, Rashed LA, Hassen MT (2018) Melatonin improves the therapeutic role of mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 28: 529-538. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2018.1471634.
88. Metwally MMM, Ebraheim LLM, Galal AAA (2018) Potential therapeutic role of melatonin on STZ-induced diabetic central neuropathy: A biochemical, histopathological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Acta Histochem. 120: 828-836. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2018.09.008.
89. Liu S, Guo Y, Yuan Q, Pan Y, Wang L, Liu Q, Wang F, Wang J, Hao A (2015) Melatonin prevents neural tube defects in the offspring of diabetic pregnancy. J. Pineal Res. 59: 508-517. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12282.
90. Gao Y, Bai C, Zheng D, Li C, Zhang W, Li M, Guan W, Ma Y (2016) Combination of melatonin and Wnt-4 promotes neural cell differentiation in bovine amniotic epithelial cells and recovery from spinal cord injury. J. Pineal Res. 60: 303-312. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12311.
91. Yoo DY, Kim W, Lee CH, Shin BN, Nam SM, Choi JH, Won MH, Yoon YS, Hwang IK (2012) Melatonin improves D-galactose-induced aging effects on behavior, neurogenesis, and lipid peroxidation in the mouse dentate gyrus via increasing pCREB expression. J. Pineal Res. 52: 21-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00912.x.
92. Wongchitrat P, Lansubsakul N, Kamsrijai U, Sae-Ung K, Mukda S, Govitrapong P (2016) Melatonin attenuates the high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced reduction in rat hippocampal neurogenesis. Neurochem. Int. 100: 97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.09.006.
93. Guo YL, Chakraborty S, Rajan SS, Wang R, Huang F (2010) Effects of oxidative stress on mouse embryonic stem cell proliferation, apoptosis, senescence, and self-renewal. Stem Cells Dev. 19: 1321-1331. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0313.
94. Furio AM., Fontao R, Falco N, Ruiz JI, Caccuri R, Cardinali DP.(2008) Neuroprotective Effect of Melatonin on Glucocorticoid Toxicity in the Rat Hippocampus. Open Physiol. J. 1: 23-27. doi: 10.2174/1874360900901010023.
95. Ruksee N, Tongjaroenbuangam W, Mahanam T, Govitrapong P (2014) Melatonin pretreatment prevented the effect of dexamethasone negative alterations on behavior and hippocampal neurogenesis in the mouse brain. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 143: 72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.02.011.
96. Fu J, Zhao SD, Liu HJ, Yuan QH, Liu SM, Zhang YM, Ling EA, Hao AJ (2011) Melatonin promotes proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells subjected to hypoxia in vitro. J. Pineal Res. 51: 104-112. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00867.x.
97. Permpoonputtana K, Tangweerasing P, Mukda S, Boontem P, Nopparat C, Govitrapong P (2018) Long-term administration of melatonin attenuates neuroinflammation in the aged mouse brain. EXCLI J. 17: 634-646. doi: 10.17179/excli2017-654.
98. Ghareghani M, Sadeghi H, Zibara K, Danaei N, Azari H, Ghanbari A (2017) Melatonin increases oligodendrocyte differentiation in cultured neural stem cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 37: 1319-1324. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0450-4.
99. Manda K,Reiter RJ (2010) Melatonin maintains adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive functions after irradiation. Prog. Neurobiol. 90: 60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.10.019.
100. Chen BH, Park JH, Lee TK, Song M, Kim H, Lee JC, Kim YM, Lee CH, Hwang IK, Kang IJ, Yan BC, Won MH, Ahn JH (2018) Melatonin attenuates scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment via protecting against demyelination through BDNF-TrkB signaling in the mouse dentate gyrus. Chem. Biol. Interact. 285: 8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.023.
101. Aranarochana A, Chaisawang P, Sirichoat A, Pannangrong W, Wigmore P, Welbat JU (2019) Protective effects of melatonin against valproic acid-induced memory impairments and reductions in adult rat hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuroscience 406: 580-593. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.02.022.
102. Sirichoat A, Krutsri S, Suwannakot K, Aranarochana A, Chaisawang P, Pannangrong W, Wigmore P, Welbat JU (2019) Melatonin protects against methotrexate-induced memory deficit and hippocampal neurogenesis impairment in a rat model. Biochem. Pharmacol. 163: 225-233. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.02.010.
103. Han J, Ji C, Guo Y, Yan R, Hong T, Dou Y, An Y, Tao S, Qin F, Nie J, Ji C, Wang H, Tong J, Xiao W, Zhang J (2017) Mechanisms underlying melatonin-mediated prevention of fenvalerate-induced behavioral and oxidative toxicity in zebrafish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 80: 1331-1341. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2017.1384167.
104. Garcia-Cabrerizo R,Garcia-Fuster MJ (2016) Comparative effects of amphetamine-like psychostimulants on rat hippocampal cell genesis at different developmental ages. Neurotoxicology 56: 29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2016.06.014.
105. Takashima Y,Mandyam CD (2018) The role of hippocampal adult neurogenesis in methamphetamine addiction. Brain Plast. 3: 157-168. doi: 10.3233/BPL-170058.
106. Dutta RR, Taffe MA, Mandyam CD (2018) Chronic administration of amphetamines disturbs development of neural progenitor cells in young adult nonhuman primates. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 85: 46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.03.023.
107. Singhakumar R, Boontem P, Ekthuwapranee K, Sotthibundhu A, Mukda S, Chetsawang B, Govitrapong P (2015) Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced inhibition of neurogenesis in the adult mouse hippocampus: An in vivo study. Neurosci. Lett. 606: 209-214. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.09.011.
108. Ekthuwapranee K, Sotthibundhu A, Govitrapong P (2015) Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced inhibition of proliferation of adult rat hippocampal progenitor cells in vitro. J. Pineal Res. 58: 418-428. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12225.
109. Ekthuwapranee K, Sotthibundhu A, Tocharus C, Govitrapong P (2015) Melatonin ameliorates dexamethasone-induced inhibitory effects on the proliferation of cultured progenitor cells obtained from adult rat hippocampus. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 145: 38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.10.003.
110. Dorostkar MM, Zou C, Blazquez-Llorca L, Herms J (2015) Analyzing dendritic spine pathology in Alzheimer's disease: problems and opportunities. Acta Neuropathol. 130: 1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1449-5.
111. Dominguez-Alonso A, Valdes-Tovar M, Solis-Chagoyan H, Benitez-King G (2015) Melatonin stimulates dendrite formation and complexity in the hilar zone of the rat hippocampus: participation of the Ca++/Calmodulin complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16: 1907-1927. doi: 10.3390/ijms16011907.
112. Hill AS, Sahay A, Hen R (2015) Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 40: 2368-2378. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.85.
113. Oglodek EA, Just MJ, Szromek AR, Araszkiewicz A (2016) Melatonin and neurotrophins NT-3, BDNF, NGF in patients with varying levels of depression severity. Pharmacol. Rep. 68: 945-951. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2016.04.003.
114. Haridas S, Kumar M, Manda K (2012) Chronic melatonin administration mitigates behavioral dysfunction induced by gamma-irradiation. Horm. Behav. 62: 621-627. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.09.006.
115. Lee Y, Lee S, Lee SR, Park K, Hong Y, Lee M, Park S, Jin Y, Chang KT, Hong Y (2014) Beneficial effects of melatonin combined with exercise on endogenous neural stem/progenitor cells proliferation after spinal cord injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15: 2207-2222. doi: 10.3390/ijms15022207.
116. Liu J, Somera-Molina KC, Hudson RL, Dubocovich ML (2013) Melatonin potentiates running wheel-induced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult C3H/HeN mice hippocampus. J. Pineal Res. 54: 222-231. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12023.
117. Spires-Jones TL,Ritchie CW (2018) A brain boost to fight Alzheimer's disease. Science 361: 975-976. doi: 10.1126/science.aau8060.
118. Michalski D, Hofmann S, Pitsch R, Grosche J, Hartig W (2017) Neurovascular specifications in the Alzheimer-like brain of mice affected by focal cerebral ischemia: implications for future therapies. J. Alzheimers Dis. 59: 655-674. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170185.
119. Tang Y, Cai B, Yuan F, He X, Lin X, Wang J, Wang Y, Yang GY (2014) Melatonin pretreatment improves the survival and function of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells after focal cerebral ischemia. Cell Transplant. 23: 1279-1291. doi: 10.3727/096368913x667510.
120. Lin L, Huang QX, Yang SS, Chu J, Wang JZ, Tian Q (2013) Melatonin in Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14: 14575-14593. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714575.
121. Tang YP, Ma YL, Chao CC, Chen KY, Lee EH (1998) Enhanced glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression upon (-)-deprenyl and melatonin treatments. J. Neurosci. Res. 53: 593-604. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19980901)53:5<593::AID-JNR9>3.0.CO;2-4.
122. Borlongan CV, Yamamoto M, Takei N, Kumazaki M, Ungsuparkorn C, Hida H, Sanberg PR, Nishino H (2000) Glial cell survival is enhanced during melatonin-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia. FASEB J. 14: 1307-1317. doi: 10.1096/fj.14.10.1307.
123. Heneka MT, Carson MJ, Khoury JE, Landreth GE , Brosseron F , Feinstein DL , Jacobs AH , Wyss-Coray T , Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM, Herrup K , Frautschy SA , Finsen B, Brown GC, Verkhratsky A, Yamanaka K , Koistinaho J, Latz E, Halle A, Petzold GC , Town T, Morgan D, Shinohara ML, Perry VH, Holmes C, Bazan NG, Brooks DJ, Hunot S, Joseph B, Deigendesch N, Garaschuk O, Boddeke E, Dinarello CA , Breitner JC, Cole GM, Golenbock DT, Kummer MP (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol. 14: 388‐405. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(15)70016-5.
124. Kalamakis G, Brüne D, Ravichandran S, Bolz J, Fan W, Ziebell F, Stiehl T, Catalá-Martinez F, Kupke J, Zhao S, Llorens-Bobadilla E, Bauer K Limpert S, Berger B, Christen U, Schmezer P, Mallm JP, Berninger B, Anders S, Sol AD, Marciniak-Czochra A, Martin-Villalba A (2019) Quiescence modulates stem cell maintenance and regenerative capacity in the aging brain. Cell 176: 1407-1419.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.040.
125. E L, Burns JM, Swerdlow RH. (2014) Effect of high-intensity exercise on aged mouse brain mitochondria, neurogenesis, and inflammation. Neurobiol. Aging 35: 2574‐2583. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging..05.033
126. Valero J, Bernardino L, Cardoso FL, Silva AP, Fontes-Ribeiro C, Ambrósio AF, Malva JO (2017) Impact of neuroinflammation on hippocampal neurogenesis: relevance to aging and Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 60: S161-S168. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170239
127. Kohman RA, Rhodes JS (2013) Neurogenesis, inflammation and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 27: 22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.09.003
128. Hu X, Leak RK, Shi Y, Suenaga J, Gao Y, Zheng P, Chen J (2015) Microglial and macrophage polarization—new prospects for brain repair. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 11: 56-64. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.207.
129. Xia Y, Chen S, Zeng S, Zhao Y, Zhu C, Deng B, Zhu G, Yin Y, Wang W, Hardeland R, Ren W (2019) Melatonin in macrophage biology: Current understanding and future perspectives. J. Pineal Res. 66: e12547. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12547.
130. Chinchalongporn V, Shukla M, Govitrapong P (2018) Melatonin ameliorates Abeta42 -induced alteration of betaAPP-processing secretases via the melatonin receptor through the Pin1/GSK3beta/NF-kappaB pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Pineal Res. 64: e12470. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12470.
131. de la Fuente Revenga M, Fernandez-Saez N, Herrera-Arozamena C, Morales-Garcia JA, Alonso-Gil S, Perez-Castillo A, Caignard DH, Rivara S, Rodriguez-Franco MI (2015) Novel N-acetyl bioisosteres of melatonin: melatonergic receptor pharmacology, physicochemical studies, and phenotypic assessment of their neurogenic potential. J. Med. Chem. 58: 4998-5014. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00245.
132. Sompol P, Liu X, Baba K, Paul KN, Tosini G, Iuvone PM, Ye K (2011) N-acetylserotonin promotes hippocampal neuroprogenitor cell proliferation in sleep-deprived mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108: 8844-8849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105114108.
133. Tosini G, Baba K, Hwang CK, Iuvone PM (2012) Melatonin: an underappreciated player in retinal physiology and pathophysiology. Exp. Eye Res. 103: 82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2012.08.009.
134. Manda K, Ueno M, Anzai K (2008) Space radiation-induced inhibition of neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and memory impairment in mice: ameliorative potential of the melatonin metabolite, AFMK. J. Pineal Res. 45: 430-438. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00611.x.
135. Manda K, Ueno M, Anzai K (2009) Cranial irradiation-induced inhibition of neurogenesis in hippocampal dentate gyrus of adult mice: attenuation by melatonin pretreatment. J. Pineal Res. 46: 71-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00632.x.
136. Soumier A, Banasr M, Lortet S, Masmejean F, Bernard N, Kerkerian-Le-Goff L, Gabriel C, Millan MJ, Mocaer E, Daszuta A (2009) Mechanisms contributing to the phase-dependent regulation of neurogenesis by the novel antidepressant, agomelatine, in the adult rat hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 2390-2403. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.72.
137. Yucel A, Yucel N, Ozkanlar S, Polat E, Kara A, Ozcan H, Gulec M (2016) Effect of agomelatine on adult hippocampus apoptosis and neurogenesis using the stress model of rats. Acta Histochem. 118: 299-304. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2016.02.007.
138. Fu W, Xie H, Laudon M, Zhou S, Tian S, You Y (2016) Piromelatine ameliorates memory deficits associated with chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 233: 2229-2239. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4272-3.
139. Figueiro-Silva J, Antequera D, Pascual C, de la Fuente Revenga M, Volt H, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Rodriguez-Franco MI, Carro E (2018) The melatonin analog IQM316 may induce adult hippocampal neurogenesis and preserve recognition memories in mice. Cell Transplant. 27: 423-437. doi: 10.1177/0963689717721217.
140. Thompson PM, Hayashi KM, Dutton RA, Chiang MC, Leow AD, Sowell ER, De Zubicaray G, Becker JT, Lopez OL, Aizenstein HJ, Toga AW (2007) Tracking Alzheimer's disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1097: 183-214. doi: 10.1196/annals.1379.017.
141. Taupin P (2006) Neurogenesis and Alzheimer's disease. Drug Target Insights 1: 1-4.
142. Leyssen M, Ayaz D, Hebert SS, Reeve S, De Strooper B, Hassan BA (2005) Amyloid precursor protein promotes post-developmental neurite arborization in the Drosophila brain. EMBO J. 24: 2944-2955. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600757.
143. Hornsten A, Lieberthal J, Fadia S, Malins R, Ha L, Xu X, Daigle I, Markowitz M, O'Connor G, Plasterk R, Li C (2007) APL-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans protein related to the human beta-amyloid precursor protein, is essential for viability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104: 1971-1976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603997104.
144. Hung AY, Koo EH, Haass C, Selkoe DJ (1992) Increased expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein during neuronal differentiation is not accompanied by secretory cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89: 9439-9443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9439.
145. Salbaum JM,Ruddle FH (1994) Embryonic expression pattern of amyloid protein precursor suggests a role in differentiation of specific subsets of neurons. J. Exp. Zool. 269: 116-127. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402690205.
146. Feng R, Rampon C, Tang YP, Shrom D, Jin J, Kyin M, Sopher B, Miller MW, Ware CB, Martin GM, Kim SH, Langdon RB, Sisodia SS, Tsien JZ (2001) Deficient neurogenesis in forebrain-specific presenilin-1 knockout mice is associated with reduced clearance of hippocampal memory traces. Neuron 32: 911-926. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00523-2.
147. Wen PH, Shao X, Shao Z, Hof PR, Wisniewski T, Kelley K, Friedrich VL, Jr., Ho L, Pasinetti GM, Shioi J, Robakis NK, Elder GA (2002) Overexpression of wild type but not an FAD mutant presenilin-1 promotes neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 10: 8-19. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2002.0490.
148. Donovan MH, Yazdani U, Norris RD, Games D, German DC, Eisch AJ (2006) Decreased adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 495: 70-83. doi: 10.1002/cne.20840.
149. Zhang C, McNeil E, Dressler L, Siman R (2007) Long-lasting impairment in hippocampal neurogenesis associated with amyloid deposition in a knock-in mouse model of familial Alzheimer's disease. Exp. Neurol. 204: 77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.09.018.
150. Zhou JN, Liu RY, Kamphorst W, Hofman MA, Swaab DF (2003) Early neuropathological Alzheimer's changes in aged individuals are accompanied by decreased cerebrospinal fluid melatonin levels. J. Pineal Res. 35: 125-130. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-079x.2003.00065.x.
151. Komuro Y, Xu G, Bhaskar K, Lamb BT (2015) Human tau expression reduces adult neurogenesis in a mouse model of tauopathy. Neurobiol. Aging 36: 2034-2042. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.03.002.
152. Ali T,Kim MO (2015) Melatonin ameliorates amyloid beta-induced memory deficits, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration via PI3/Akt/GSk3beta pathway in the mouse hippocampus. J. Pineal Res. 59: 47-59. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12238.
153. Deng YQ, Xu GG, Duan P, Zhang Q, Wang JZ (2005) Effects of melatonin on wortmannin-induced tau hyperphosphorylation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 26: 519-526. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00102.x.
154. Pappolla MA, Sos M, Omar RA, Bick RJ, Hickson-Bick DL, Reiter RJ, Efthimiopoulos S, Robakis NK (1997) Melatonin prevents death of neuroblastoma cells exposed to the Alzheimer amyloid peptide. J. Neurosci. 17: 1683-1690.
155. Pappolla MA, Chyan YJ, Poeggeler B, Frangione B, Wilson G, Ghiso J, Reiter RJ (2000) An assessment of the antioxidant and the antiamyloidogenic properties of melatonin: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J. Neural Transm. 107: 203-231. doi: 10.1007/s007020050018.
156. Olcese JM, Cao C, Mori T, Mamcarz MB, Maxwell A, Runfeldt MJ, Wang L, Zhang C, Lin X, Zhang G, Arendash GW (2009) Protection against cognitive deficits and markers of neurodegeneration by long-term oral administration of melatonin in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. J. Pineal Res. 47: 82-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00692.x.
157. Suh J, Choi SH, Romano DM, Gannon MA, Lesinski AN, Kim DY, Tanzi RE (2013) ADAM10 missense mutations potentiate beta-amyloid accumulation by impairing prodomain chaperone function. Neuron 80: 385-401. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.08.035.
158. Ryan MM, Morris GP, Mockett BG, Bourne K, Abraham WC, Tate WP, Williams JM (2013) Time-dependent changes in gene expression induced by secreted amyloid precursor protein-alpha in the rat hippocampus. BMC Genomics 14: 376. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-376.
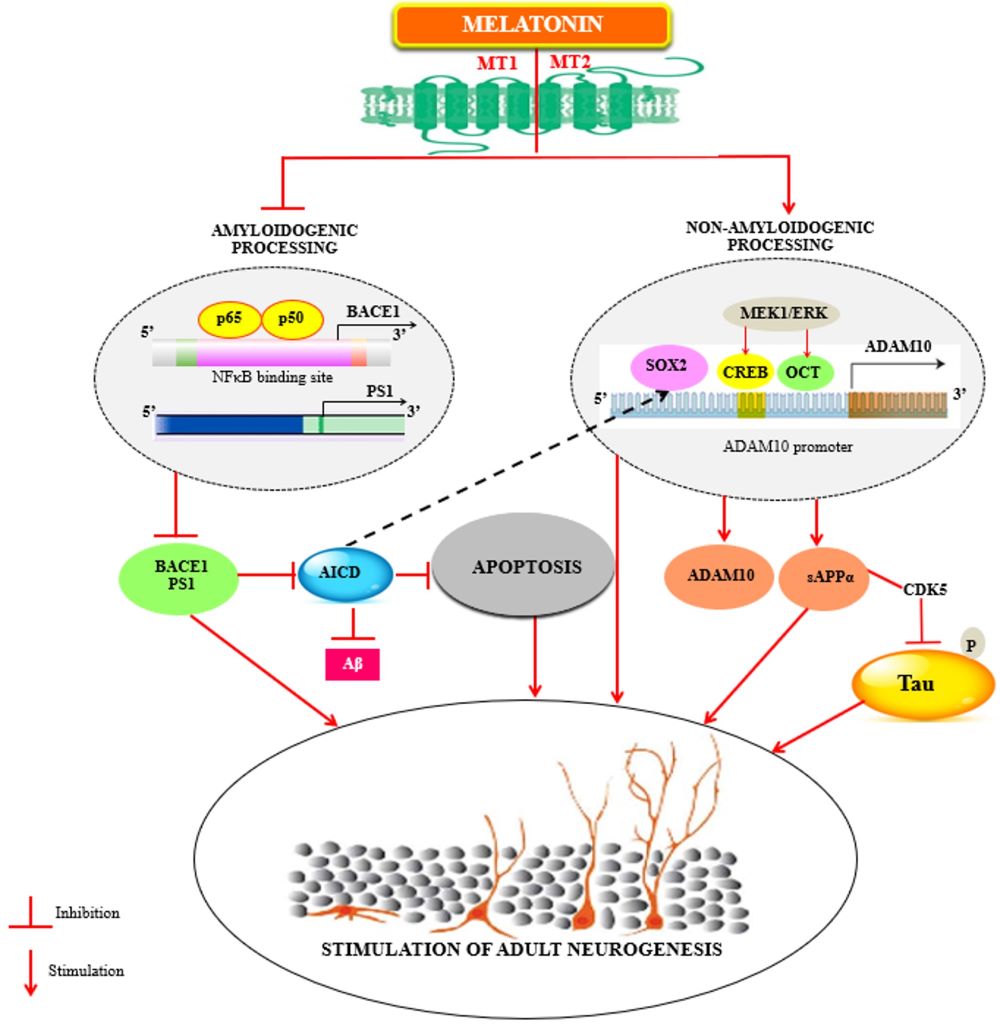
159. Shukla M, Htoo HH, Wintachai P, Hernandez JF, Dubois C, Postina R, Xu H, Checler F, Smith DR, Govitrapong P, Vincent B (2015) Melatonin stimulates the nonamyloidogenic processing of betaAPP through the positive transcriptional regulation of ADAM10 and ADAM17. J. Pineal Res. 58: 151-165. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12200.
160. Endres K,Deller T (2017) Regulation of alpha-secretase ADAM10 in vitro and in vivo: genetic, epigenetic, and protein-based mechanisms. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 10: 56. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00056.
161. Habib A, Sawmiller D, Tan J (2017) Restoring soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha functions as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 95: 973-991. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23823.
162. Colciaghi F, Borroni B, Pastorino L, Marcello E, Zimmermann M, Cattabeni F, Padovani A, Di Luca M (2002) [alpha]-Secretase ADAM10 as well as [alpha]APPs is reduced in platelets and CSF of Alzheimer disease patients. Mol. Med. 8: 67-74.
163. Caille I, Allinquant B, Dupont E, Bouillot C, Langer A, Muller U, Prochiantz A (2004) Soluble form of amyloid precursor protein regulates proliferation of progenitors in the adult subventricular zone. Development 131: 2173-2181. doi: 10.1242/dev.01103.
164. Demars MP, Bartholomew A, Strakova Z, Lazarov O (2011) Soluble amyloid precursor protein: a novel proliferation factor of adult progenitor cells of ectodermal and mesodermal origin. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 2: 36. doi: 10.1186/scrt77.
165. Lazarov O,Demars MP (2012) All in the family: How the APPs regulate neurogenesis. Front. Neurosci. 6: 81. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00081.
166. Mattson MP (1997) Cellular actions of beta-amyloid precursor protein and its soluble and fibrillogenic derivatives. Physiol. Rev. 77: 1081-1132. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1997.77.4.1081.
167. Gakhar-Koppole N, Hundeshagen P, Mandl C, Weyer SW, Allinquant B, Muller U, Ciccolini F (2008) Activity requires soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha to promote neurite outgrowth in neural stem cell-derived neurons via activation of the MAPK pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 28: 871-882. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06398.x.
168. Ohsawa I, Takamura C, Morimoto T, Ishiguro M, Kohsaka S (1999) Amino-terminal region of secreted form of amyloid precursor protein stimulates proliferation of neural stem cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11: 1907-1913. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00601.x.
169. Bell KF, Zheng L, Fahrenholz F, Cuello AC (2008) ADAM-10 over-expression increases cortical synaptogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 29: 554-565. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.11.004.
170. Han P, Dou F, Li F, Zhang X, Zhang YW, Zheng H, Lipton SA, Xu H, Liao FF (2005) Suppression of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activation by amyloid precursor protein: a novel excitoprotective mechanism involving modulation of tau phosphorylation. J. Neurosci. 25: 11542-11552. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3831-05.2005.
171. Curtis MA, Faull RL, Eriksson PS (2007) The effect of neurodegenerative diseases on the subventricular zone. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8: 712-723. doi: 10.1038/nrn2216.
172. Ayuso-Sacido A, Moliterno JA, Kratovac S, Kapoor GS, O'Rourke DM, Holland EC, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Roy NS, Boockvar JA (2010) Activated EGFR signaling increases proliferation, survival, and migration and blocks neuronal differentiation in post-natal neural stem cells. J. Neurooncol. 97: 323-337. doi: 10.1007/s11060-009-0035-x.
173. Chen Q, Nakajima A, Choi SH, Xiong X, Sisodia SS, Tang YP (2008) Adult neurogenesis is functionally associated with AD-like neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 29: 316-326. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2007.09.005.
174. Ghosal K, Stathopoulos A, Pimplikar SW (2010) APP intracellular domain impairs adult neurogenesis in transgenic mice by inducing neuroinflammation. PLoS One 5: e11866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011866.
175. Sarlak G, Htoo HH, Hernandez JF, Iizasa H, Checler F, Konietzko U, Song W, Vincent B (2016) Sox2 functionally interacts with betaAPP, the betaAPP intracellular domain and ADAM10 at a transcriptional level in human cells. Neuroscience 312: 153-164. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.11.022.
176. Sarlak G,Vincent B (2016) The roles of the stem cell-controlling Sox2 transcription factor: from neuroectoderm development to Alzheimer's disease? Mol. Neurobiol. 53: 1679-1698. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9123-4.
177. Wei R, Zhao X, Hao H, Du W, Zhu H (2016) Embryonic stem-like cells from rabbit blastocysts cultured with melatonin could differentiate into three germ layers in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 83: 1003-1014. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22739.
178. Hu X, Das B, Hou H, He W, Yan R (2018) BACE1 deletion in the adult mouse reverses preformed amyloid deposition and improves cognitive functions. J. Exp. Med. 215: 927-940. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171831.
179. Chatila ZK, Kim E, Berle C, Bylykbashi E, Rompala A, Oram MK, Gupta D, Kwak SS, Kim YH, Kim DY, Choi SH, Tanzi RE (2018) BACE1 regulates proliferation and neuronal differentiation of newborn cells in the adult hippocampus in mice. eNeuro 5: doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0067-18.2018.
180. Gadadhar A, Marr R, Lazarov O (2011) Presenilin-1 regulates neural progenitor cell differentiation in the adult brain. J. Neurosci. 31: 2615-2623. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4767-10.2011.
181. Bonds JA, Kuttner-Hirshler Y, Bartolotti N, Tobin MK, Pizzi M, Marr R, Lazarov O (2015) Presenilin-1 dependent neurogenesis regulates hippocampal learning and memory. PLoS One 10: e0131266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131266.
182. Panmanee J, Nopparat C, Chavanich N, Shukla M, Mukda S, Song W, Vincent B, Govitrapong P (2015) Melatonin regulates the transcription of betaAPP-cleaving secretases mediated through melatonin receptors in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J. Pineal Res. 59: 308-320. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12260.
183. Mukda S, Panmanee J, Boontem P, Govitrapong P (2016) Melatonin administration reverses the alteration of amyloid precursor protein-cleaving secretases expression in aged mouse hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 621: 39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.013.
184. Karasek K., Winczyk K (2006) Melatonin in humans. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 57: 19–39.
185. Di WL, Kadva A, Johnston A, Silman R (1997) Variable bioavailability of oral melatonin. N. Engl. J. Med. 336: 1028–1029. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199704033361418.
186. Brusco LI, Márquez M, Cardinali DP (2000) Melatonin treatment stabilizes chronobiologic and cognitive symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 21: 39‐42.
187. Kilic E, Kilic U, Bacigaluppi M, Guo Z, Ben Abdallah N, Wolfer DP, Reiter RJ, Hermann DM, Bassetti CL (2008) Delayed melatonin administration promotes neuronal survival, neurogenesis and motor recovery, and attenuates hyperactivity and anxiety after mild focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Pineal Res. 45: 142–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00568.x.
188. López-Armas G, Flores-Soto ME, Chaparro-Huerta V, Jave-Suarez LF, Soto-Rodríguez S, Rusanova I, Acuña-Castroviejo D, González-Perez O, González-Castañeda RE (2016) Prophylactic role of oral melatonin administration on neurogenesis in adult Balb/c mice during rem sleep deprivation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016:2136902. doi:10.1155/2016/2136902.
189. Ramírez-Rodríguez G, Klempin F, Babu H. Benítez-King G, Kempermann G (2009) Melatonin modulates cell survival of new neurons in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. 34: 2180–2191. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.46.
190. Zhdanova IV, Geiger DA, Schwagerl AL, Leclair OU, Killiany R, Taylor JA, Rosene DL, Moss MB, Madras BK (2002) Melatonin promotes sleep in three species of diurnal nonhuman primates. Physiol. Behav. 75: 523-529. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(02)00654-6.
191. Polimeni G, Esposito E, Bevelacqua V, Guarneri C, Cuzzocrea S (2014) Role of melatonin supplementation in neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 19: 429–446. doi: 10.2741/4217.
192. Tordjman S, Chokron S, Delorme R, Charrier A, Bellissant E, Jaafari N , Fougerou (2017) Melatonin: pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 15: 434‐443. doi:10.2174/1570159X14666161228122115.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


