Melatonin: An anticancer molecule in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A mechanistic review
Melatonin: An anticancer molecule in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Several factors impact the mortality rate of patients with gastrointestinal cancers including late diagnosis, metastases to distance sites, and lack of efficacy of the conventional therapies. To reduce mortality rate, the novel effective remedies should be explored. Melatonin is an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and oncostatic molecule and has been showed potential in controlling various malignancies. In the gastrointestinal tract, melatonin plays an important role via its membrane receptors of MT1 and MT2. It can diminish esophageal lesions resulting from acid–pepsin–bile contact and also inhibits expression of myosin light chain kinase as well as reduces its activity by regulating extracellular signal-transduction of protein kinase. The aim of the present study was to review the critical functions of melatonin in the prevention and treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma including its influence on gastrointestinal pathology, oncostatic role and potential mechanisms. Particularly, the inhibitory function of melatonin on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its therapeutic effects are summarized. We suggest that melatonin co-treatment will enhance the efficacy of conventional treatments and survival times in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
References
2. Pourhanifeh MH, Mehrzadi S, Kamali M, Hosseinzadeh A (2020) Melatonin and gastrointestinal cancers: Current evidence based on underlying signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol.886: 173471.
3. Jung B, Ahmad N. Melatonin in cancer management: progress and promise. Cancer Res. 2006;66(20):9789-93.
4. Su SC, Hsieh MJ, Yang WE, Chung WH, Reiter RJ, Yang SF. (2017) Cancer Metastasis: Mechanisms of inhibition by melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 62 (1): e12370.
5. Zhao D, Yu Y, Shen Y, Liu Q, Zhao Z, Sharma R, et al. (2019) Melatonin synthesis and function: evolutionary history in animals and plants. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 10: 249.
6. Brzozowski T, Jaworek J. (2014) Editorial (Thematic issues: Basic and clinical aspects of melatonin in the gastrointestinal tract. new advancements and future perspectives). Curr. Pharm. Des. 20 (30): 4785-4787.
7. Kandil TS, Mousa AA, El-Gendy AA, Abbas AM. (2010) The potential therapeutic effect of melatonin in gastro-esophageal reflux disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 10 (1): 1-9.
8. Lerner AB, Case JD, Takahashi Y, Lee TH, Mori W. (1958) Isolation of melatonin, the pineal gland factor that lightens melanocyteS1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80 (10): 2587.
9. Tan D-X, Zheng X, Kong J, Manchester LC, Hardeland R, Kim SJ, et al. (2014) Fundamental issues related to the origin of melatonin and melatonin isomers during evolution: relation to their biological functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15 (9): 15858-15890.
10. Paredes SD, Korkmaz A, Manchester LC, Tan D-X, Reiter RJ. (2009) Phytomelatonin: a review. J. Exp. Bot. 60 (1): 57-69.
11. Reiter RJ, Tan D-x, Manchester LC, Simopoulos AP, Maldonado MD, Flores LJ, et al. (2007) Melatonin in edible plants (phytomelatonin): identification, concentrations, bioavailability and proposed functions. World. Rev. Nutr. Diet. 97: 211-230.
12. Manchester LC, Coto‐Montes A, Boga JA, Andersen LPH, Zhou Z, Galano A, et al. (2015) Melatonin: an ancient molecule that makes oxygen metabolically tolerable. J. Pineal Res. 59 (4): 403-419.
13. Suofu Y, Li W, Jean-Alphonse FG, Jia J, Khattar NK, Li J, et al. (2017) Dual role of mitochondria in producing melatonin and driving GPCR signaling to block cytochrome c release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 114 (38): E7997-E8006.
14. Huether G, Poeggeler B, Reimer A, George A. (1992) Effect of tryptophan administration on circulating melatonin levels in chicks and rats: evidence for stimulation of melatonin synthesis and release in the gastrointestinal tract. Life Sci. 51 (12): 945-953.
15. Guney Y, Hicsonmez A, Uluoglu C, Guney H, Ozel Turkcu U, Take G, et al. (2007) Melatonin prevents inflammation and oxidative stress caused by abdominopelvic and total body irradiation of rat small intestine. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 40: 1305-1314.
16. Trivedi P, Jena G. (2013) Melatonin reduces ulcerative colitis-associated local and systemic damage in mice: investigation on possible mechanisms. Dig. Dis. Sci. 58 (12): 3460-3474.
17. Li Y, Li S, Zhou Y, Meng X, Zhang J-J, Xu D-P, et al. (2017) Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Oncotarget 8 (24): 39896.
18. Bubenik GA. (2002) Gastrointestinal melatonin: localization, function, and clinical relevance. Dig. Dis. Sci. 47 (10): 2336-2348.
19. Bubenik GA. (2001) Localization, physiological significance and possible clinical implication of gastrointestinal melatonin. Neurosignals 10 (6): 350-366.
20. Kvetnoy IM, Ingel IE, Kvetnaia TV, Malinovskaya NK, Rapoport SI, Raikhlin NT, et al. (2002) Gastrointestinal melatonin: cellular identification and biological role. Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 23 (2): 121-132.
21. Brzozowska I, Strzalka M, Drozdowicz D, J Konturek S, Brzozowski T. (2014) Mechanisms of esophageal protection, gastroprotection and ulcer healing by melatonin. Implications for the therapeutic use of melatonin in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcer disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 20 (30): 4807-4815.
22. Radwan P, Skrzydlo-Radomanska B, Radwan-Kwiatek K, Burak-Czapiuk B, Strzemecka J. (2009) Is melatonin involved in the irritable bowel syndrome. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 60 (Suppl 3): 67-70.
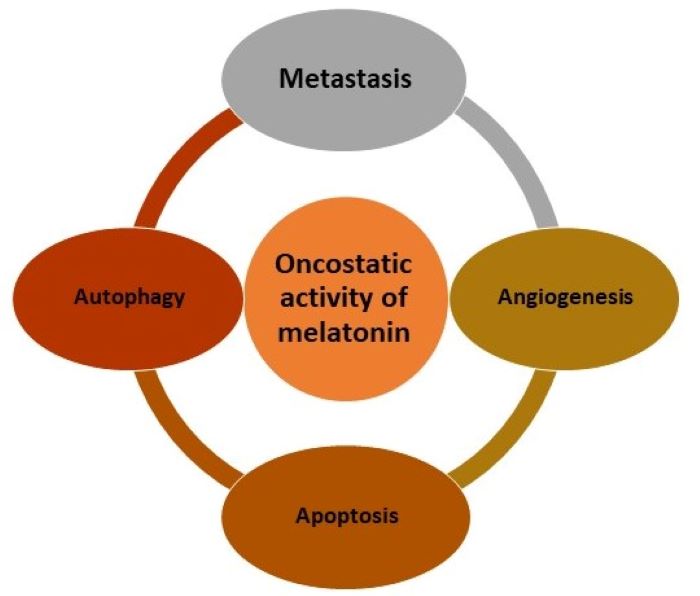
23. Targhazeh N, Reiter RJ, Rahimi M, Qujeq D, Yousefi T, Shahavi MH, et al. (2022) Oncostatic activities of melatonin: Roles in cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy. Biochimie 202: 34-48.
24. Kohandel Z, Farkhondeh T, Aschner M, Samarghandian S. (2021) Molecular targets for the management of gastrointestinal cancer using melatonin, a natural endogenous body hormone. Biomed. Pharmacother. 140: 111782.
25. Ahmed R, Mahavadi S, Al-Shboul O, Bhattacharya S, Grider JR, Murthy KS. (2013) Characterization of signaling pathways coupled to melatonin receptors in gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Regul. Pept. 184: 96-103.
26. Pal PK, Chattopadhyay A, Bandyopadhyay D. (2021) Functional interplay of melatonin in the bile duct and gastrointestinal tract to mitigate disease development: An overview. Melatonin Res. 4 (1): 118-140.
27. Niu G, Yousefi B, Qujeq D, Marjani A, Asadi J, Wang Z, et al. (2021) Melatonin and doxorubicin co-delivered via a functionalized graphene-dendrimeric system enhances apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Bol. Appl. 119: 111554.
28. Chascsa D, Carey EJ, Lindor KD. (2017) Old and new treatments for primary biliary cholangitis. Liver Int. 37 (4): 490-499.
29. McMillin M, DeMorrow S, Glaser S, Venter J, Kyritsi K, Zhou T, et al. (2017) Melatonin inhibits hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone release and reduces biliary hyperplasia and fibrosis in cholestatic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 313 (5): G410-G418.
30. Vimalraj S, Saravanan S, Raghunandhakumar S, Anuradha D. (2020) Melatonin regulates tumor angiogenesis via miR-424-5p/VEGFA signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. Life Sci. 256: 118011.
31. Marques JH, Mota AL, Oliveira JG, Lacerda JZ, Stefani JP, Ferreira LC, et al. (2018) Melatonin restrains angiogenic factors in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting miR-152-3p: In vivo and in vitro studies. Life Sci. 208: 131-138.
32. Dai M, Cui P, Yu M, Han J, Li H, Xiu R. (2008) Melatonin modulates the expression of VEGF and HIF‐1α induced by CoCl2 in cultured cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 44 (2): 121-126.
33. Park SY, Jang WJ, Yi EY, Jang JY, Jung Y, Jeong JW, et al. (2010) Melatonin suppresses tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting HIF‐1α stabilization under hypoxia. J. Pineal Res. 48 (2): 178-184.
34. Kim KJ, Choi JS, Kang I, Kim KW, Jeong CH, Jeong JW. (2013) Melatonin suppresses tumor progression by reducing angiogenesis stimulated by HIF‐1 in a mouse tumor model. J. Pineal Res. 54 (3): 264-270.
35. Jardim-Perassi BV, Arbab AS, Ferreira LC, Borin TF, Varma NR, Iskander A, et al. (2014) Effect of melatonin on tumor growth and angiogenesis in xenograft model of breast cancer. PloS one 9 (1): e85311.
36. León J, Casado J, Jiménez Ruiz SM, Zurita MS, González‐Puga C, Rejón JD, et al. (2014) Melatonin reduces endothelin‐1 expression and secretion in colon cancer cells through the inactivation of FoxO‐1 and NF‐κβ. J. Pineal Res. 56 (4): 415-426.
37. Borin TF, Arbab AS, Gelaleti GB, Ferreira LC, Moschetta MG, Jardim‐Perassi BV, et al. (2016) Melatonin decreases breast cancer metastasis by modulating Rho‐associated kinase protein‐1 expression. J. Pineal Res. 60 (1): 3-15.
38. Lin YW, Lee LM, Lee WJ, Chu CY, Tan P, Yang YC, et al. (2016) Melatonin inhibits MMP‐9 transactivation and renal cell carcinoma metastasis by suppressing Akt‐MAPK s pathway and NF‐κB DNA‐binding activity. J. Pineal Res. 60 (3): 277-290.
39. Mao L, Dauchy RT, Blask DE, Dauchy EM, Slakey LM, Brimer S, et al. (2016) Melatonin suppression of aerobic glycolysis (Warburg effect), survival signalling and metastasis in human leiomyosarcoma. J. Pineal Res. 60 (2): 167-177.
40. Proietti S, Cucina A, Dobrowolny G, D'Anselmi F, Dinicola S, Masiello MG, et al. (2014) Melatonin down‐regulates MDM 2 gene expression and enhances p53 acetylation in MCF‐7 cells. J. Pineal Res. 57 (1): 120-129.
41. Wei JY, Li WM, Zhou LL, Lu QN, He W. (2015) Melatonin induces apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through HDAC 4 nuclear import mediated by C a MKII inactivation. J. Pineal Res. 58 (4): 429-438.
42. Leja‐Szpak A, Jaworek J, Pierzchalski P, Reiter RJ. (2010) Melatonin induces pro‐apoptotic signaling pathway in human pancreatic carcinoma cells (PANC‐1). J. Pineal Res. 49 (3): 248-255.
43. Qu H, Xue Y, Lian W, Wang C, He J, Fu Q, et al. (2018) Melatonin inhibits osteosarcoma stem cells by suppressing SOX9-mediated signaling. Life Sci. 207: 253-264.
44. Liu R, Wang H-l, Deng M-j, Wen X-j, Mo Y-y, Chen F-m, et al. (2018) Melatonin inhibits reactive oxygen species-driven proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and vasculogenic mimicry in oral cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018: 3510970.
45. Ji G, Zhou W, Li X, Du J, Li X, Hao H. (2021) Melatonin inhibits proliferation and viability and promotes apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells via upregulation of the microRNA-34a/449a cluster. Mol. Med. Rep. 23 (3): 187.
46. Yang YC, Chiou PC, Chen PC, Liu PY, Huang WC, Chao CC, et al. (2019) Melatonin reduces lung cancer stemness through inhibiting of PLC, ERK, p38, β‐catenin, and Twist pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 34 (2): 203-209.
47. Zhang J, Xie T, Zhong X, Jiang H-L, Li R, Wang B-Y, et al. (2020) Melatonin reverses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cisplatin chemoresistance by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY).12 (6): 5423-5438.
48. Oskoii MA, Khatami N, Majidinia M, Rezazadeh M-A, Mir SM, Sadeghpour A, et al. (2020) Serum level of melatonin in patients with osteoarthritis and its relation with 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine and vitamin D. J. Res. Clin. Med. 8 (1): 34.
49. Mir SM, Yousefi B, Marjani A, Rahimi M, Qujeq D. (2020) The sensitization of melatonin in osteosarcoma cells by suppression of anti-apoptotic proteins. Pharmaceutical Sci. 26 (2): 159-164.
50. Zheng Y, Tu J, Wang X, Yu Y, Li J, Jin Y, et al. (2019) The therapeutic effect of melatonin on GC by inducing cell apoptosis and autophagy induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Onco Targets Ther. 12: 10187.
51. Chok KC, Koh RY, Ng MG, Ng PY, Chye SM. (2021) Melatonin induces autophagy via reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Molecules 26 (16): 5038.
52. Moniruzzaman M, Ghosal I, Das D, Chakraborty SB. (2018) Melatonin ameliorates H2O2-induced oxidative stress through modulation of Erk/Akt/NFkB pathway. Biol. Res. 51. (1):17.
53. Mir SM, Aliarab A, Goodarzi G, Shirzad M, Jafari SM, Qujeq D, et al. (2022) Melatonin: A smart molecule in the DNA repair system. Cell Biochem. Funct. 40 (1): 4-16.
54. Chuffa LGA, Fioruci-Fontanelli BA, Mendes LO, Seiva FRF, Martinez M, Fávaro WJ, et al. (2015) Melatonin attenuates the TLR4-mediated inflammatory response through MyD88-and TRIF-dependent signaling pathways in an in vivo model of ovarian cancer. BMC cancer 15 (1): 1-13.
55. Chuffa LG, Alves MS, Martinez M, Camargo IC, Pinheiro PF, Domeniconi RF, et al. (2016) Apoptosis is triggered by melatonin in an in vivo model of ovarian carcinoma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 23 (2): 65-76.
56. Song J, Ma S-J, Luo J-H, Zhang H, Wang R-X, Liu H, et al. (2018) Melatonin induces the apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells via blockade of the AKT/MDM2 pathway. Oncol. Rep. 39 (4): 1975-1983.
57. Wang J, Xiao X, Zhang Y, Shi D, Chen W, Fu L, et al. (2012) Simultaneous modulation of COX‐2, p300, Akt, and Apaf‐1 signaling by melatonin to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 53 (1): 77-90.
58. Bubenik G. (2008) Thirty four years since the discovery. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 59 (2): 33-51.
59. Galano A, Tan D-X, Reiter RJ. (2018) Melatonin: a versatile protector against oxidative DNA damage. Molecules 23 (3): 530.
60. Moradkhani F, Moloudizargari M, Fallah M, Asghari N, Heidari Khoei H, Asghari MH. (2020) Immunoregulatory role of melatonin in cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 235 (2): 745-757.
61. Perfilyeva YV, Ostapchuk YO, Abdolla N, Tleulieva R, Krasnoshtanov VC, Belyaev NN. (2019) Exogenous melatonin up-regulates expression of CD62L by lymphocytes in aged mice under inflammatory and non-inflammatory conditions. Immunol. Invest. 48 (6): 632-643.
62. Gao Y, Xiao X, Zhang C, Yu W, Guo W, Zhang Z, et al. (2017) Melatonin synergizes the chemotherapeutic effect of 5‐fluorouracil in colon cancer by suppressing PI 3K/AKT and NF‐κB/iNOS signaling pathways. J. Pineal Res. 62 (2): e12380.
63. Akbarzadeh M, Movassaghpour AA, Ghanbari H, Kheirandish M, Maroufi NF, Rahbarghazi R, et al. (2017) The potential therapeutic effect of melatonin on human ovarian cancer by inhibition of invasion and migration of cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 7 (1): 1-11.
64. Lin PH, Tung YT, Chen HY, Chiang YF, Hong HC, Huang KC, et al. (2020) Melatonin activates cell death programs for the suppression of uterine leiomyoma cell proliferation. J. Pineal Res. 68 (1): e12620.
65. Liu L, Pan Y, Chen D, Xia L, Liu Y, Xingyu P, et al. (2017) Melatonin Inhibits the Proliferation of Human MG-63 Osteosarcoma Cells via Downregulation of Cyclins and CDKs. J. China Med. Univ. 46 (2): 131-135.
66. Alonso-González C, Menéndez-Menéndez J, González-González A, González A, Cos S, Martínez-Campa C. (2018) Melatonin enhances the apoptotic effects and modulates the changes in gene expression induced by docetaxel in MCF‑7 human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 52 (2): 560-570.
67. Lacerda JZ, Ferreira LC, Lopes BC, Aristizábal-Pachón AF, Bajgelman MC, Borin TF, et al. (2019) Therapeutic potential of melatonin in the regulation of MiR-148a-3p and angiogenic factors in breast cancer. Microrna 8 (3): 237-247.
68. Carbajo-Pescador S, Ordoñez R, Benet M, Jover R, García-Palomo A, Mauriz J, et al. (2013) Inhibition of VEGF expression through blockade of Hif1 α and STAT3 signalling mediates the anti-angiogenic effect of melatonin in HepG2 liver cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 109 (1): 83-91.
69. Mannino G, Caradonna F, Cruciata I, Lauria A, Perrone A, Gentile C. (2019) Melatonin reduces inflammatory response in human intestinal epithelial cells stimulated by interleukin‐1β. J. Pineal Res. 67 (3): e12598.
70. Hevia D, Gonzalez-Menendez P, Fernandez-Fernandez M, Cueto S, Rodriguez-Gonzalez P, Garcia-Alonso JI, et al. (2017) Melatonin decreases glucose metabolism in prostate cancer cells: a 13C stable isotope-resolved metabolomic study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18 (8): 1620.
71. Lu Y-X, Chen D-L, Wang D-S, Chen L-Z, Mo H-Y, Sheng H, et al. (2016) Melatonin enhances sensitivity to fluorouracil in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma through inhibition of Erk and Akt pathway. Cell Death Dis. 7 (10): e2432.
72. Tan J, Wang Y, Xia Y, Zhang N, Sun X, Yu T, et al. (2014) Melatonin protects the esophageal epithelial barrier by suppressing the transcription, expression and activity of myosin light chain kinase through ERK1/2 signal transduction. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 34 (6): 2117-2127.
73. Gu H, Shen Q, Mei D, Yang Y, Wei R, Ni M. (2020) Melatonin inhibits TE-1 esophageal cancer cells metastasis by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and decreasing MMP-9. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 50 (1): 65-72.
74. Konturek S, Zayachkivska O, Havryluk X, Brzozowski T, Sliwowski Z, Pawlik M, et al. (2007) Protective influence of melatonin against acute esophageal lesions involves prostaglandins, nitric oxide and sensory nerves. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 58 (2): 361.
75. Patrick L. (2011) Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a review of conventional and alternative treatments. Altern. Med. Rev. 16 (2): 116-133.
76. Pereira RdS. (2006) Regression of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms using dietary supplementation with melatonin, vitamins and aminoacids: comparison with omeprazole. J. Pineal Res.41(3): 195-200.
77. Mo F,Bai YH, Zhou Y, Cai XH, Li BP (2003) Inhibitory effect of melatonin on Eca-109 cells of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Xi'an jiao tong da xue xue bao Yi xue ban. 4: 384.
78. Di Bella G, Madarena M. (2009) Complete objective response of oesophageal squamocellular carcinoma to biological treatment. Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 30 (3): 312-321.
79. Sánchez-Barceló E, Mediavilla M, Tan DX, Reiter R. (2010) Clinical uses of melatonin: evaluation of human trials. Curr. Med. Chem. 17 (19): 2070-2095.
80. Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Sainz RM, Mayo JC, Lopez‐Burillo S. (2002) Melatonin: reducing the toxicity and increasing the efficacy of drugs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 54 (10): 1299-1321.
81. Lagergren J, Lagergren P. (2010) Oesophageal cancer. BMJ 341: c6280.
82. Coleman HG, Xie S-H, Lagergren J. (2018) The epidemiology of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 154 (2): 390-405.
83. Klupińska G, Wiśniewska-Jarosińska M, Harasiuk A, Chojnacki C, Stec-Michalska K, Błasiak J, et al. (2006) Nocturnal secretion of melatonin in patients with upper digestive tract disorders. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 57: 41-50.
84. Konturek S, Konturek P, Brzozowska I, Pawlik M, Sliwowski Z, Cześnikiewicz-Guzik M, et al. (2007) Localization and biological activities of melatonin. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 58 (3): 381-405.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
For all articles published in Melatonin Res., copyright is retained by the authors. Articles are licensed under an open access Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, meaning that anyone may download and read the paper for free. In addition, the article may be reused and quoted provided that the original published version is cited. These conditions allow for maximum use and exposure of the work, while ensuring that the authors receive proper credit.
In exceptional circumstances articles may be licensed differently. If you have specific condition (such as one linked to funding) that does not allow this license, please mention this to the editorial office of the journal at submission. Exceptions will be granted at the discretion of the publisher.


